other comprehensive income что это
Other Comprehensive Income
What is Other Comprehensive Income?
What’s included in Other Comprehensive Income?
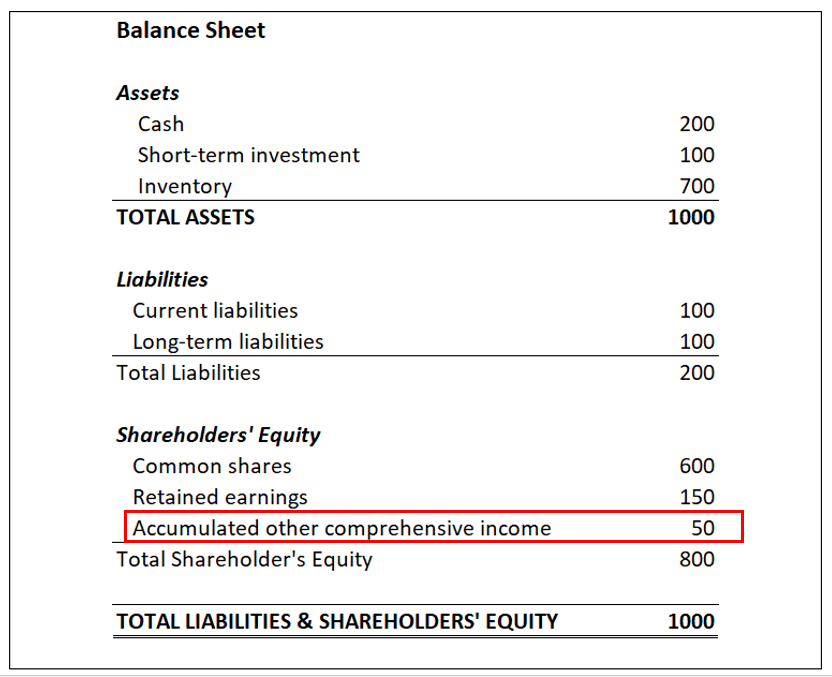
Other comprehensive income is shown on a company’s balance sheet. It is similar to retained earnings, which is impacted by net income, except it includes those items that are excluded from net income. This helps reduce the volatility of net income as the value of unrealized gains/losses moves up and down.
Common items included in the account include:
Reporting Standards for Other Comprehensive Income
Only unrealized items are recorded as other comprehensive income. Once the transaction has been realized (e.g., the company’s investments have been sold), it must be removed from the company’s balance sheet and recognized as a realized gain/loss on the income statement.
Importance of Other Comprehensive Income
Other comprehensive income is a crucial financial analysis metric for a more inclusive evaluation of a company’s earnings and overall profitability. While the income statement remains a primary indicator of the company’s profitability, other comprehensive income improves the reliability and transparency of financial reporting.
The other income information cannot uncover the company’s day-to-day operations, but it can provide insight on other essential items. For example, an analyst can obtain insight regarding the management of the company’s investments. The reported investments’ unrealized gains/losses may forecast the company’s actual, realized gains or losses on its investments.
Also, if a company runs overseas operations, the other income section can contribute to the understanding of the dynamics of the company’s foreign operations and assess the impact of foreign exchange fluctuations. Finally, it helps determine the extent to which a company’s future pension liabilities may affect unrealized profits.
Related Readings
CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA) Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI’s Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! ® Become a Certified Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® CFI’s Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® certification will help you gain the confidence you need in your finance career. Enroll today! certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
Free Accounting Courses
Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s free online accounting classes.
These courses will give the confidence you need to perform world-class financial analyst work. Start now!
Building confidence in your accounting skills is easy with CFI courses! Enroll now for FREE to start advancing your career!
Отчет о совокупном доходе входит в состав основной внутренней информации о компании, которую финансовый аналитик рассматривает при анализе доходов, расходов, прибыли, убытков и других финансовых результатов компании за определенный период. Рассмотрим концепцию и пример этого отчета в рамках изучения анализа финансовой отчетности по программе CFA.
Volkswagen Group выбрала вторую форму представления.
Отчет о прибыли или убытке.
Отчет о прибыли или убытке (или отчет о прибылях и убытках, англ. ‘income statement’) представляет информацию о финансовых показателях (результатах) деятельности компании за определенный период времени. Он сообщает, сколько выручки и прочих доходов компания получила в течение периода, а также, какие расходы она понесла, чтобы обеспечить эту выручку и прочие доходы.
Выручка (англ. ‘revenue’), как правило, означает денежные суммы, взимаемые за поставку товаров или услуг в ходе обычной деятельности компании.
Прочие доходы (англ. ‘other income’) могут включать в себя как доходы, возникающие в ходе обычной деятельности, так и другие доходы, такие, как прибыль от отчуждения бизнеса.
Расходы (англ. ‘expenses’) отражают оттоки, уменьшающие активы компании и возникновение обязательств, уменьшающих собственный капитал. Расходы, как правило, включают в себя такие статьи, как себестоимость реализованной продукции (стоимость проданных товаров), административные расходы, расходы по налогу на прибыль, и также могут включать убытки.
Чистая прибыль (выручка + прочие доходы минус расходы) по отчету о прибылях и убытках часто упоминаются как «нижняя строка» (англ. ‘bottom line’) из-за его близость к нижней части прибылей и убытков.
Чистая прибыль (англ. ‘net income’) также может упоминаться как «net earnings», «net profit» и «profit or loss» (т.е. прибыль или убыток). В том случае, если расходы превышают выручку и прочие доходы, результат упоминается как «чистый убыток» (англ. ‘net loss’).
Основное уравнение, лежащее в основе отчета о прибылях и убытках:
Отчеты о прибылях и убытках представляются на консолидированной основе. Это означает, что они включают в себя доходы и расходы дочерних компаний, находящихся под контролем материнской (отчитывающейся) компании.
В общих чертах, когда одна компания (материнская) контролирует другую компанию (дочернюю), материнская компания представляет в финансовой отчетности собственную информацию, консолидированную с информацией этой дочерней компании.
Если материнская компания владеет более чем 50% голосующих акций дочерней компании, это означает, что она контролирует дочернюю компанию и, таким образом, она должна представлять консолидированную финансовую отчетность.
Каждая строка консолидированного отчета о прибылях и убытках включает в себя полную сумму из соответствующей строки отчета о прибылях и убытках дочерней компании (после исключения всех внутригрупповых операций). Однако, если материнская компания не владеет 100% долей дочерней компании, материнской компании необходимо представлять распределение чистой прибыли по долям миноритарных владельцев.
Доли миноритарных владельцев (англ. ‘minority interests’), называемые также неконтролирующими долями участия (англ. ‘non-controlling interests’), принадлежат владельцам остальных акций дочерней компании, которые не принадлежат материнской компании. Доля консолидированной чистой прибыли, приходящаяся на миноритариев, указывается в нижней части отчета о прибылях и убытках, вместе с чистой прибылью, приходящейся на владельцев материнской компании.
Практический пример отчета о прибыли или убытке.
В Иллюстрации 5 представлен годовой отчет о прибыли или убытке Volkswagen Group за 2017 год.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IMG_20171216_182148727_LL-4f9a9d7d74714f95b116a7182aa20ecf.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/AmyImage-AmyDrury-d6b6143c6d5c49a0add2201e25969457.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/AmandaJackson-05f6b53318ed407aab6eea61a3d7fdf6.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cfa_candidate_guide__ryan_fuhrmann-5bfc2622c9e77c005142f4ca.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CharleneRhinehartHeadshot-CharleneRhinehart-ca4b769506e94a92bc29e4acc6f0f9a5.jpg)