reconciliation account sap что это
What is SAP Reconciliation Account?

The SAP general ledger is linked to the sub ledgers. For every transaction posted in the sub ledger, the same value will be updated to the corresponding reconciliation account.
Creating SAP Reconciliation Account
SAP reconciliation accounts are created very similar to all other general ledger accounts. There are just a few attributes that need to be set correctly. Transaction code FS00 is used to create reconciliation accounts centrally.
In this tutorial, we will not walk through the entire account creation process, as a reconciliation account is created in much the same way as any other general ledger account. Instead, let’s examine account 160000 for AP (Accounts Payable) reconciliation. We will walk through the three main areas where a reconciliation account differs from other accounts.
To display a reconciliation account use transaction code FS00 or you can use the following menu path:
You will be taken to the screen below: 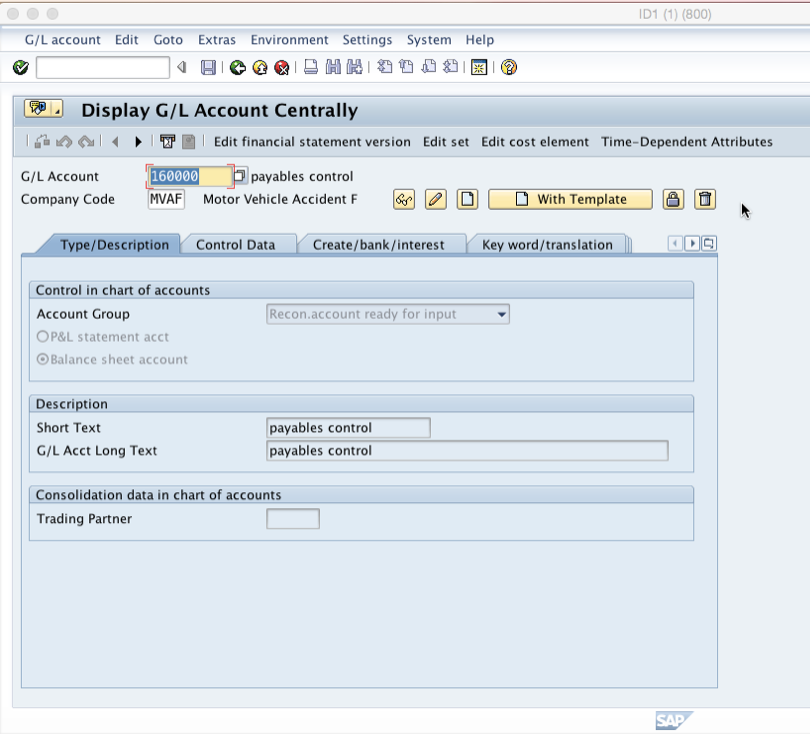
The first area that denotes that this is a reconciliation account is the control data in the “Type/Description” tab. Here, you should note that the account group “Recon.account ready for input” is selected. Also, all reconciliation accounts should be identified as balance sheet accounts: 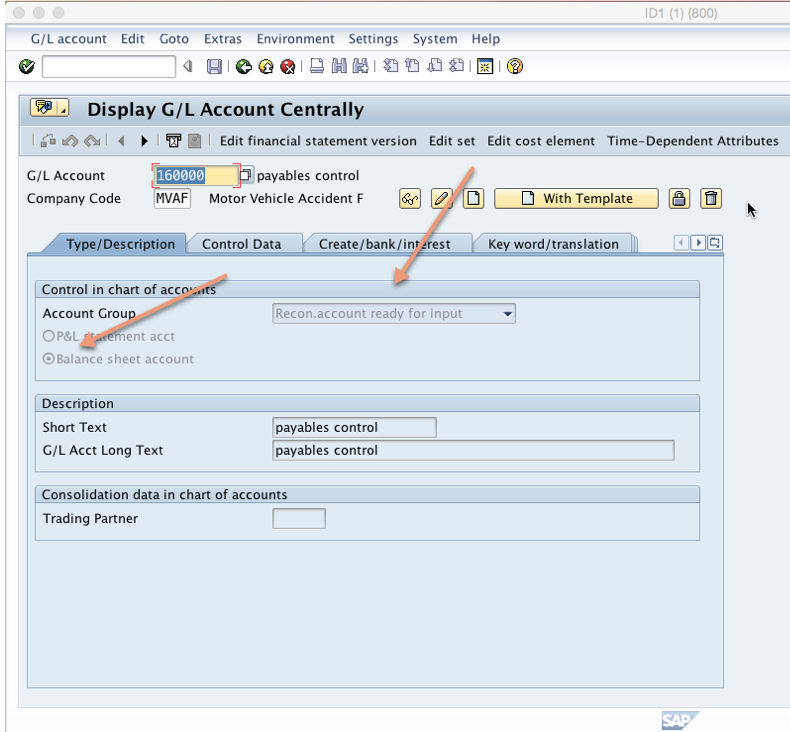
Click on “Control Data” tab and check the second area that has to be maintained when creating a reconciliation account. In the field “Recon.account for acct type” you select between assets, customers and vendors to specify which sub ledger the account reconciles: 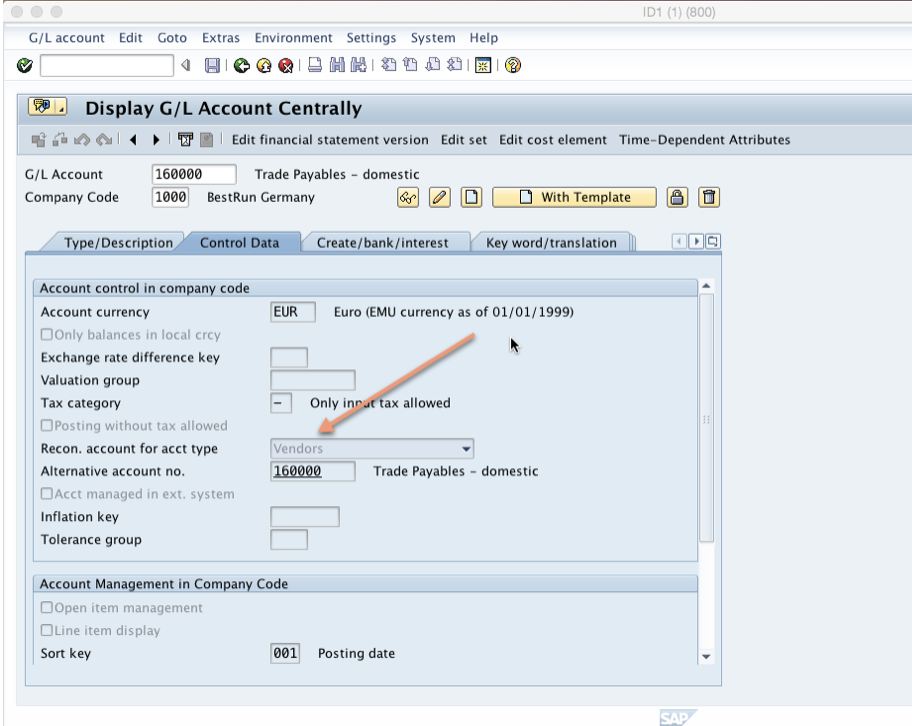
Finally, click on “Create/bank/interest” tab and check the field status group. The field status group for all reconciliation accounts is G067: 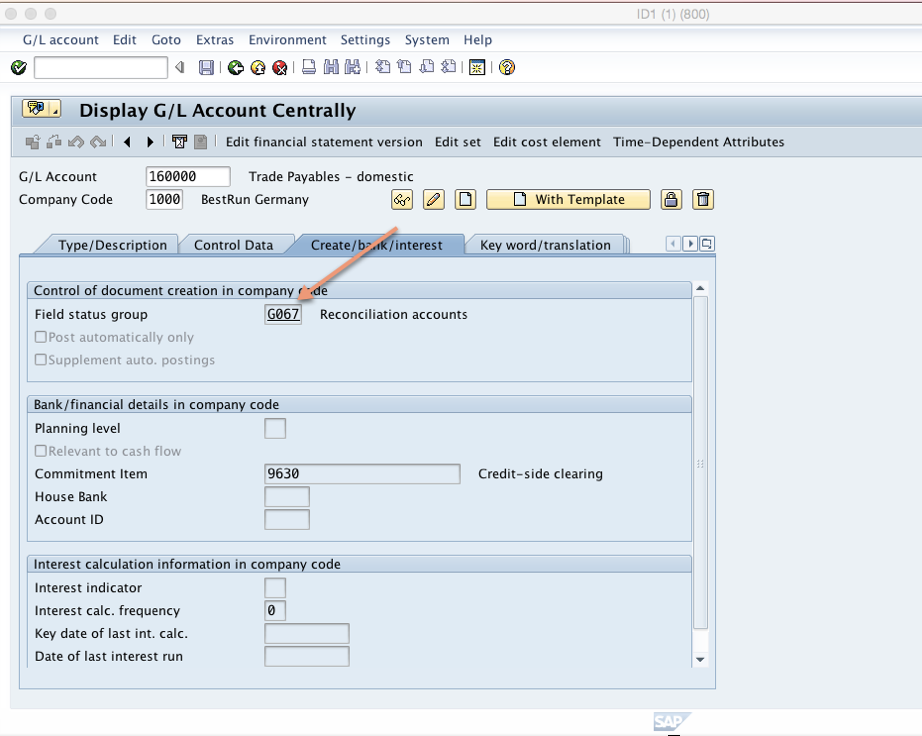
Assigning SAP Reconciliation Account to Sub Ledger Account
Now that we have seen how to set up a reconciliation account, complete the process by learning how to assign it to a sub ledger account. Each sub ledger account has to be linked to a certain reconciliation account for its postings to be recognized in the financial statements. Let’s see how it’s done by looking at an already created vendor.
Use transaction code FK03 to display a vendor or use the the following menu path:
You will be taken to the screen below: 
Enter a valid company code and vendor number, select the “Accounting info” tick box and press enter. The reconciliation account 160000 examined earlier is assigned in the “Recon. account” field for this vendor: 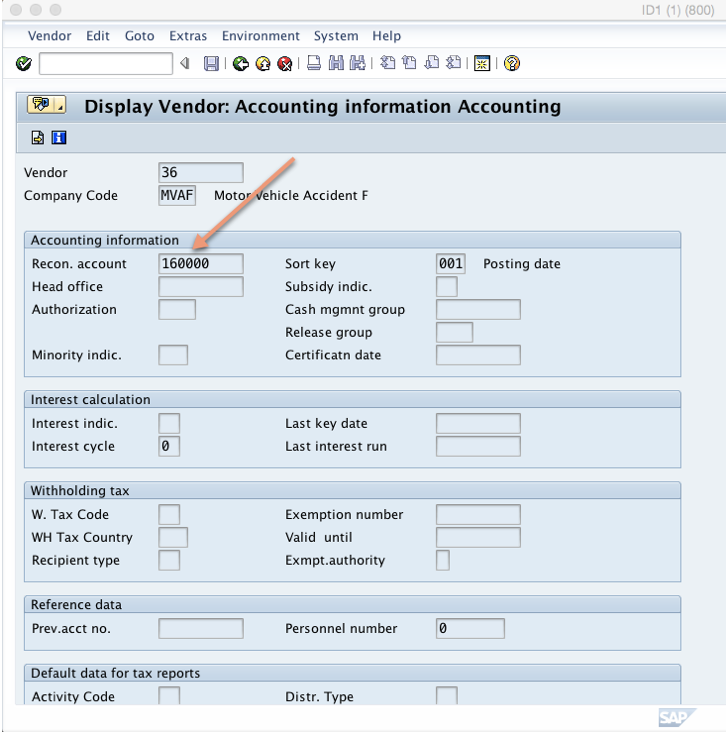
The result is that for every posting recorded under vendor 36, the general ledger updates with the same amount via reconciliation account 160000.
Posting a Vendor Invoice
Finally, let’s see how a reconciliation account is updated when you post an invoice for a vendor.
To post a vendor invoice use transaction code FB60 or you can use the following menu path:
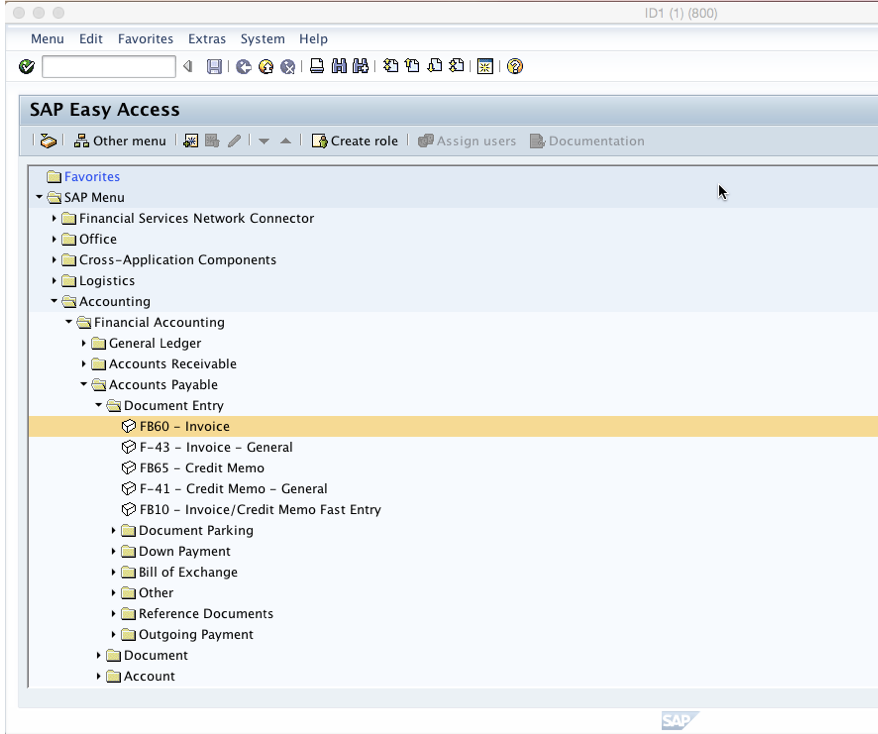
Fill in the vendor number examined above (vendor 36 in our case) and all details necessary for posting an invoice: 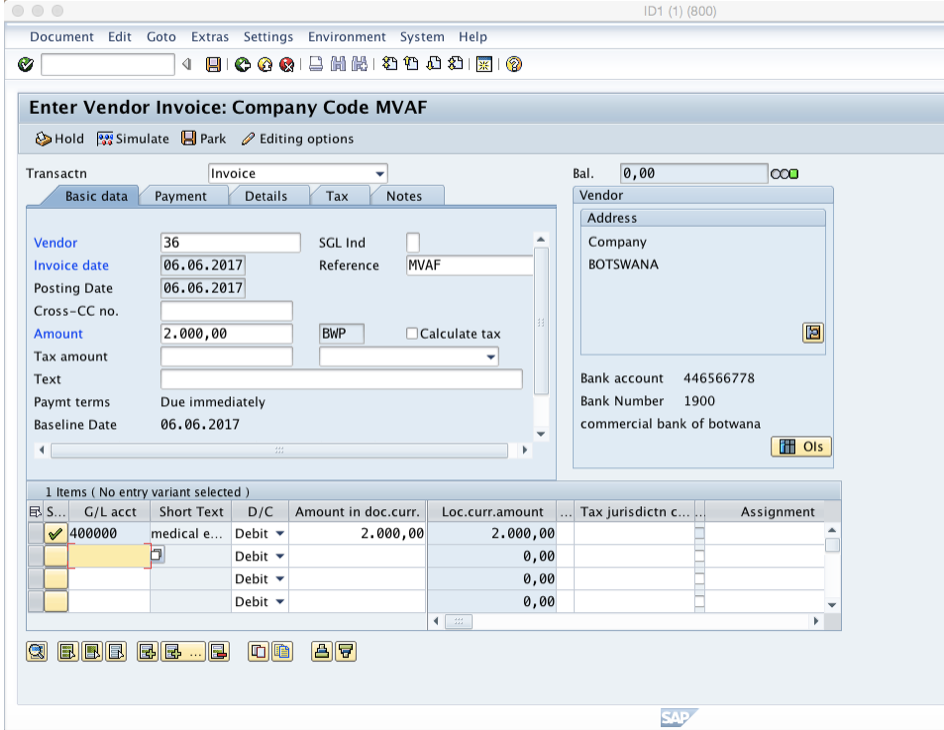
Now post the invoice and click “Document > Display” on the top far left of the toolbar to display the created document: 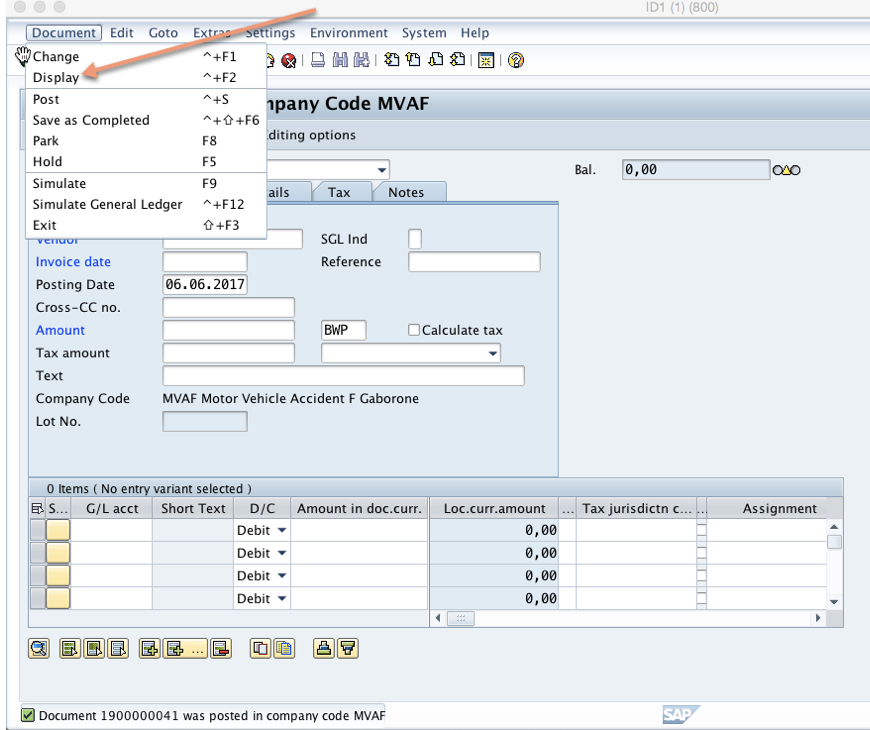
You will see the following screen. Here you see that vendor 36 has been credited with 2000 BWP. Click on general ledger view: 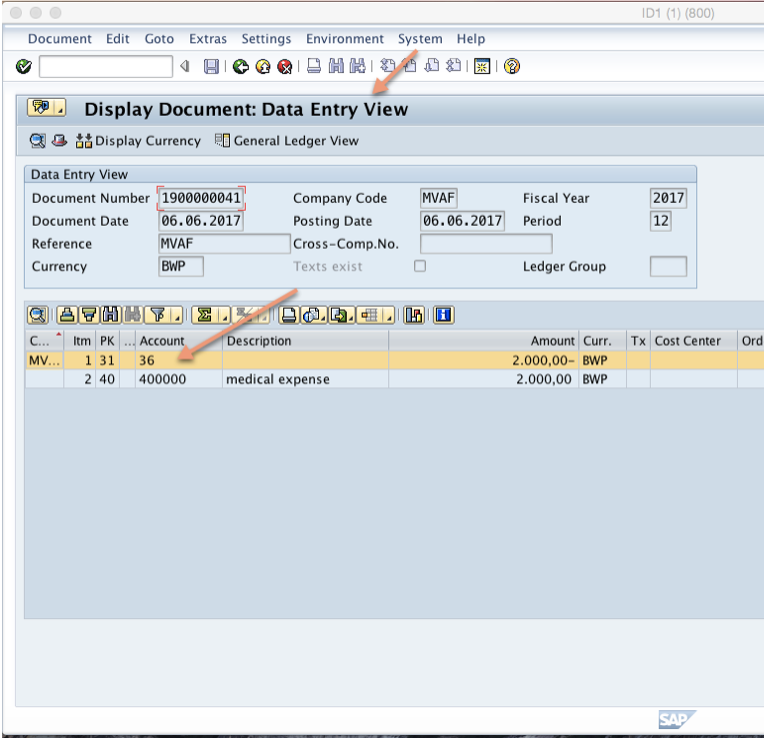
You can see the reconciliation account 160000 assigned to the vendor account is updated by the transaction above: 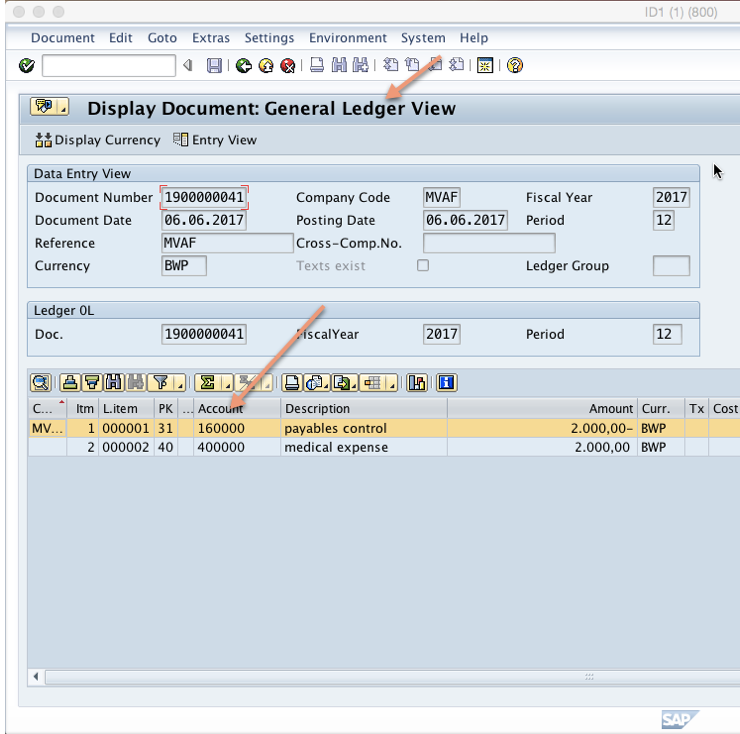
The end result is that reconciliation account 160000 was also credited with 2000 BWP. Therefore, every time you post a transaction to a sub ledger account the reconciliation account will be updated with the same amount in real time. In order to maintain a clean reconciliation with the sub ledger, SAP reconciliation account can only be updated by the system through the sub ledger. Direct posting to SAP reconciliation account is prohibited by the system.
Related Posts
9 thoughts on “What is SAP Reconciliation Account?”
Here the recon account itself is the GL account. So when vendor posting is done, credit to vendor account is automatically posted to associated recon GL account (160000). Please note that that the recon account is just a name given to the GL account which is used as a posting account for all the vendor sub-accounts. We cannot create reports and statements out of thousands of sub-GLs so attach a GL to each of them and name it as recon account. Thanks.
I downloaded a debtors age analysis for a recon account. now the balance has changed due to entries that were posted. instead of generating a new F.99, is there a way that a line item can be displayed so that i can see what are the entries that went through?
If I want to reconcile AP sub ledger with GL, Which report should I run on SAP for AP sub ledger to compare with GL report for reconciliation purpose or what’s the procedure for doing AP- GL reconciliation
Recon account should be credited in the above case..
The subledger transactions will be
Dr Purchase or Expense
Cr Vendor
In GL you will not have the list of vendors but a few reconciliation accounts like Domestic Vendors, Foreign Vendors etc. So for transaction above the GL View will be as below
Dr Purchase or Expense
Cr Reconciliation Account.
This means when SAP posts crediting the vendor in the Subledger this flows to GL module will same credit to Reco account. Hope this helps
What is the use of reconciliation account in SAP FI Module?
Last Modified on June 19, 2020 by Editorial Staff
Reconciliation account in SAP is a general ledger account assigned to the business partner master record to record all transactions in the sub ledger.
Posting to the sub ledgers are automatically get posted to the assigned reconciliation account by which the general ledger will always be up to date. It is a prerequisite for creation of vendor master.
Every transaction in an account of a sub-ledger is automatically posted to the general ledger. This integration is guaranteed by the reconciliation account in SAP. It must be assigned to every customer or vendor master record.
This is done be entering the respective General Ledger account in the Reconciliation account field of the customer master record. While posting to the customer master, these accounts in SAP has following functions:
It ensures that the total of all General Ledger account balances is always zero. This is a prerequisite for creating a balance sheet at any time. Therefore, it is no longer necessary to transfer account balances from sub-ledger to General Ledger accounts, since the balances are updated automatically in the general ledger.
Via the reconciliation account in SAP, the screen lay out for posting to the customer master can be determined. For example, the fields for entering hedging transactions for foreign currency can be suppressed, if such transactions are not carried out in a company. Further Via these accounts, currencies in which the corresponding customer account should be posted can be specified.
Generally, a common reconciliation account in SAP is assigned to several customer accounts. It’s displayed on the balance sheet under the balance sheet item “Sundry Debtors”.
Several reconciliation accounts are required if you want to have different account balances separately on the balance sheet, such as domestic receivables and foreign receivables.
Note: SAP and SAP logo is a registered trademark of SAP AG in Germany and in several other countries. We are not affiliated or related to any division or subsidiary of SAP AG.
Bank Reconciliation Accounts in S/4HANA 2020
With an intention of reducing the number of GL accounts and for simplifying the payment process and cash reporting, SAP has introduced a new way of mapping house banks with GL accounts. With this new method, it is possible to assign multiple house bank accounts to the same GL account.
To facilitate this, a new GL account type called ‘Cash Account’ is provided. When user creates a GL account with account type ‘Cash Account’ another field appears called ‘GL Account subtype’. The following values are possible in this field:
Reconciliation account for house banks. You assign the required clearing accounts to this reconciliation account.
Clearing account of a bank reconciliation account for payments in transfer. When you create this subaccount, you need to enter the bank reconciliation account it is connected with.
Used for petty cash (accounts assigned in cash journal) accounts
A G/L account created with account type ‘Cash Account’ and subtype ‘B’ is called a bank reconciliation account and is the main account for carrying confirmed balances. A bank reconciliation account can be assigned to multiple house bank accounts. You can therefore, for example, decide to set one GL account each for domestic banks and foreign banks. In effect, therefore, bank account has become a sub-ledger of the main general ledger (similar to customer, vendor or asset sub-ledger).
A G/L account created with account type ‘Cash Account’ and subtype ‘S’ is called a bank clearing account. For each main bank reconciliation account created, it is possible to create one clearing bank account for each payment method. When account subtype ‘S’ is selected, you need to assign the clearing account to a main bank reconciliation account.
The new mapping is represented as shown below:
Note: It is still possible to use the previous method of managing banks and their GL accounts. In such cases the GL account type would continue to be created as ‘balance sheet account’ and not as ‘Cash Account’.
User Guidance
In the following section I will show a step-by-step user guidance to demonstrate how the system can be set up and the output expected at each step.
Step 1: Create G/L Account as bank reconciliation account
Note that new G/L Account type ‘Cash Account’ is now available. ‘Cash Account’ is specifically used for bank reconciliation account.
Also, a new field – GL Account Subtype appears when you select GL account type as ‘Cash Account’.
We select ‘B’ indicating that we are creating a main bank reconciliation account.
Output: The G/L account ‘11009990 – Sample Acct for BoA’ is created as bank reconciliation account and it is extended to company code 1710
Step 2: Create a bank clearing account
For bank clearing account also, you enter the account type as ‘Cash Account’.
Note that when you create a GL account with type as ‘Cash Account’ and subtype as ‘S – Bank Subaccount’, another field appears where we need to assign the main bank reconciliation account with the bank clearing account.
We then assign 11009990 as the main bank reconciliation account.
Also note that for each main bank reconciliation account, you need to create one bank subaccount for each payment method.
Output: Bank subaccount ‘11009991 – Bank Clr A/c-BOA’ is created which is assigned to bank reconciliation account 11009990. This account is extended to company code 1710.
Step 3: Create a bank
Create a bank using app ‘Manage Banks’
Output: Bank BoA is created with bank key BOFAUS3N001.
Step 4: Create a house bank
From the ‘House Banks’ section of the ‘Manage Bank’ app, click on ‘Create’ to create new house bank.
Enter the house bank details and assign the bank key just created
Output: House Bank BOA01 is created in company code 1710
Step 5: Create a house bank account
Create a new bank account using app ‘Manage Bank Accounts’
Output: House Bank Account BOA01 is created with account number 100001
Step 6: Assign the bank reconciliation account to house bank account.
In the ‘House Bank Account Connectivity’ tab, create a bank account connectivity by clicking on ‘Create’
Enter the bank reconciliation account created in step 1 in the field ‘G/L account’.
The indicator for ‘Bank Reconciliation Account’ turns to ‘Yes’
Output: House Bank Account BOA01 is assigned to GL account ‘11009990’ for house bank BOA01
Step 7: Assign the bank subaccount in ‘Bank Selection’ for bank customizing
When trying to assign bank subaccount in the customizing for ‘Bank Determination’, the field for Bank Subaccount is greyed out even after selection.
Note that this can be maintained in ‘Bank Accounts (Enhanced)’ tab
Output: Bank subaccount cannot be manually entered in classic ‘Bank Determination’ customizing anymore.
Step 8: Post a supplier invoice
Post a manual FI supplier invoice.
Output: Supplier invoice with document number 1900000001 is posted creating a liability line item.
Step 9: Post outgoing payment.
Use app ‘Post Outgoing Payment’ for posting invoice payment.
Enter house bank and bank account ID.
Enter the GL account. If a GL account other than 11009990 or 11009991 is entered here, the following error is shown.
Correct the GL account to 11009991
Output: Journal entry 1500000001 (2020, 1710) was saved successfully
Step 10: Assign the same bank reconciliation account to a different house bank
Create House Bank in company code 1710
Create a bank account for house bank HSB01 and assign the GL account 11009990 to it.
Inference: We can assign the same GL account 11009990 to two house bank accounts of different house banks.
Benefits (Point of View):
The new mapping architecture of bank and GL accounts is step forward in rationalizing the chart of account and simplifying the bank process as well. We can foresee several benefits of this new method:
We did not find any specific advantage of using the new account subtype ‘P’ in cash journal except that it is easier to identify in the classification of GL master data as ‘Cash Account’.
I hope this is useful in your conversations with clients on the latest S/4HANA features. Please share your opinion and feedback on this.
Reconciliation Accounts and Special G/L Indicator
Most SAP people might be asking, what is a reconciliation account in SAP Financial Accounting? Well, my dear readers surely you will be enlightened by this article.
First…
You must understand the definition of general ledger. General ledger is the main accounting record of a business which uses double-entry bookkeeping. In SAP, the central task of G/L accounting is to provide a comprehensive picture for external accounting and accounts. Transactions that have a financial impact are captured by the general ledger. The transactions could be originated from other modules. Example, posting of goods receipt (MIGO) performed by purchasing personnel (MM module) have already a financial impact. It increases the inventory balance and increases the GR/IR clearing account. The accounting journal entry the transactions MIGO create is debit (dr) Inventory account (G/L) and credit GR/IR clearing accounts (G/L).
The general ledgers summarize all financial transactions of a Company. It is the the basis of the preparation of the Company’s Financial Statements.
Now, let’s dig it further
Reconciliation Accounts are G/L accounts that receive postings from a subsidiary ledgers. Meaning, transactions data are not posted directly to recon accounts. Example of recon accounts are Accounts Receivable, Accounts Payable and Fixed Assets G/L. For accounts receivable G/L the subsidiary ledger is the customer account. All transactions with the customers are posted directly to the customer account and the recon account is automatically updated. How this thing happen? Well, when you create a customer account you specify under the Company Code data the reconciliation account.
All normal transactions to the customer e.g. sale of goods are posted to the recon account defined in the customer master data. Next question would be, what G/Laccount should be updated for postings of customer down payment (advance collection)? For proper accounting, downpayment should not be posted to Accounts Receivable – trade. It should be posted to different G/L account e.g. Advances from customer. Well, how would the said transaction be posted to Advances accounts.
This is one of the cases where the idea of special G/L indicator comes in. With the use of special G/L indicator you can specify in the set-up what G/L account advances transactions be posted. Standard posting key of customer transaction with special G/L indicator are 09 (dr) and 19 (cr). The system will always require you to indicate the special G/L indicator when you use the said posting keys.
How to use Bank Reconciliation Account in Payment Program
SAP introduces a new G/L account type C (Cash Account), which has two sub types B (Bank Reconciliation Account) and S (Bank Subaccount).This new feature can help customer significantly reduce the numbers of G/L accounts.
In this blog post I’ll guide you how to implement the new feature in payment program step by step.
Error of G/L Account Determination
Once the new bank reconciliation account is used in the house bank account, it will impact on the G/L account determination in payment program.
If you schedule a payment run then, you get an error message FZ 314 “G/L account does not exist in company code” in the log of the payment program.
Error log of payment program
Before we know how to resolve this issue, I would like to introduce the new concept of the bank reconciliation account.
Bank Reconciliation Account
Traditionally, a bank account is represented with a set of G/L accounts often constructed in the following way:
Bank GL logic at SAP
Here, G/L subaccounts on a bank current account are just like “legs on a spider.” The system must provide a set of G/L subaccounts for every bank account, thus making the number of G/L accounts huge. In some extreme cases, 70% of G/L accounts are occupied by banks.
Why can’t we re-model the relationship between a bank account and a G/L account? Just let numbers of bank accounts use one special G/L account, that is a bank reconciliation account.
Then, we just need one set of subaccounts to manage different clearing methods.
The classic G/L account representation of a bank account and the new bank reconciliation account can run side by side. It just depends on what kind of G/L account is used in the house bank account.
The new model brings the following benefits:
Definition of Bank Reconciliation Accounts and Subaccounts
SAP introduces a new G/L account type C (Cash Account) and two sub types B (Bank Account) and S (Bank Subaccount):
| Term | Definition |
| Bank Reconciliation Account | |
| Bank Subaccount |
We can log in to the system to see the new functionality. If you are a G/L accountant, you can open the app “Manage G/L Account Master Data.” Below are screenshots of a bank reconciliation account and of a bank subaccount:
Bank Reconciliation Account
Bank Sub GL Account
I will explain how to assign the house bank account to the reconciliation account in the next step.
Defining a House Bank Account
If you are a cash specialist, you can open the app “Manage Bank Account”, select a house bank account, and then go to House Bank Account Connectivity:
House Bank Account Data
If you enter a bank reconciliation account, the property “Bank Reconciliation Account” will be populated automatically.
The question then is how to find out which subaccount should be used in the payment program.
Bank Account Determination
For the automatic payment program, we can use the SSCUI Set Up Bank Determination for Payment Transactions (1010045).
It’s still possible to config the bank subaccount as a classic bank G/L account just like the house bank account DEBK2/DEAC2 in the screenshot. However, once you set a house bank account to new bank reconciliation account, just like DEBK1/DEAC1 in the screenshot, the legacy configuration of bank subaccount becomes grayed out. If you’re trying to create a new config record for DEAC1, you will find that you can’t enter a bank subaccount any more.
The last question is how to find the subaccounts for different payment methods.
Account Symbols
Configuration for account symbols reuses the functionality of Electronic Bank Statement.
Go to the configuration for Electronic Bank Statement via the SSCUI Make Global Settings for Electronic Bank Statement (101024). First, you need to create an account symbol and select the SIP (self-initiated payment) relevant checkbox.
Then, assign an overlaid rule to the account symbol.
You can now assign the account symbol to payment methods in the SSCUI Assign Account Symbol to Payment Methods (103557).
We can open the app “Manage Automatic Payments” to delete the proposal and re-run it.
The proposal and the payment document are generated on the sub G/L account successfully.
Call to Action
If you want to know more about the relevant master data and configuration maintenance, you can refer to the following links,
Defining House Bank Accounts
Assigning G/L Accounts to House Bank Accounts
Automatic Determination of Bank Subaccounts
In case of any further questions, please leave a comment below and I will try to answer you.
































