psu oracle что это
It all started in January 2005 with Critical Patch Updates (CPU). Then Patch Set Updates (PSU) were added as cumulative patches that included priority fixes as well as security fixes. As of the October 2012 Critical Patch Update, Oracle has changed the terminology to better differentiate between patch types. This terminology will be used for the Oracle Database, Enterprise Manager, Fusion Middleware, and WebLogic.
Critical Patch Update (CPU) now refers to the overall release of security fixes each quarter rather than the cumulative database security patch for the quarter. Think of the CPU as the overarching quarterly release and not as a single patch.
Patch Set Updates (PSU) are the same cumulative patches that include both the security fixes and priority fixes. The key with PSUs is they are minor version upgrades (e.g., 11.2.0.1.1 to 11.2.0.1.2). Once a PSU is applied, only PSUs can be applied in future quarters until the database is upgraded to a new base version.
Security Patch Update (SPU) terminology is introduced in the October 2012 Critical Patch Update as the term for the quarterly security patch. SPU patches are the same as previous CPU patches, just a new name. For the database, SPUs can not be applied once PSUs have been applied until the database is upgraded to a new base version.
Bundle Patches are the quarterly patches for Windows and Exadata which include both the quarterly security patches as well as recommended fixes.
References: New Patch Nomenclature for Oracle Products [ID 1430923.1]
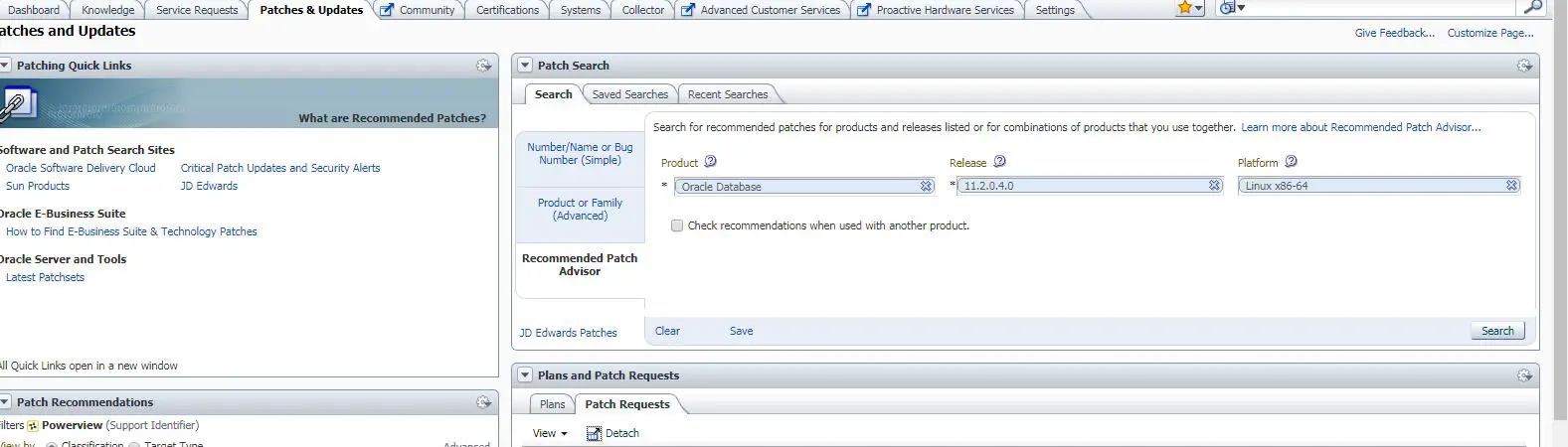
Below are the steps for applying quarterly PSU patch on Oracle 11g database.
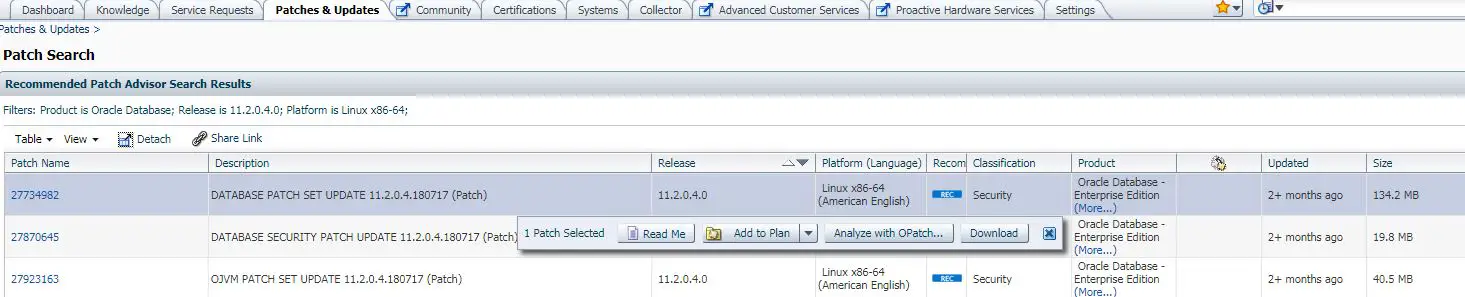
1. Download the patch from Oracle support portal.
2. Validate patch version:
opatch utility is used to apply patches to the database. So before applying patch, we need to check whether the existing opatch version is supported for the patch or not.
So refer the readme file of the patch for the minimum supported version.
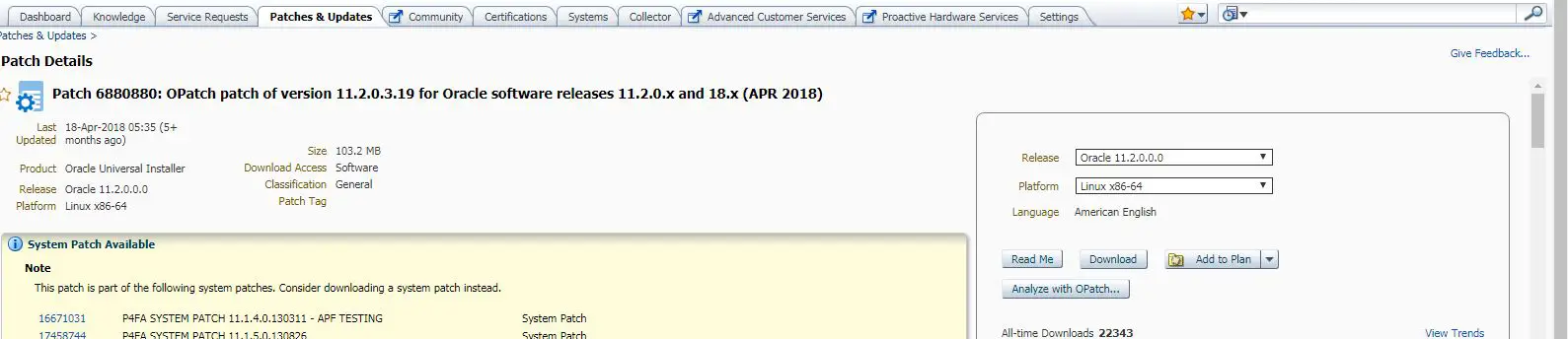
1.2.1 OPatch Utility
You must use the OPatch utility version 11.2.0.3.6 or later to apply this patch. Oracle recommends that you use the latest released OPatch version for 11.2, which is available for download from My Oracle Support patch 6880880 by selecting the 11.2.0.0.0 release.
For information about OPatch documentation, including any known issues, see My Oracle Support Document 293369.1 OPatch documentation list.
Lets check the existing opatch version in database.
Existing version is 11.2.0.3.4, lower than the required one. So we need to install the required opatch utility.
INSTALLING OPATCH UTILITY:
Download opatch utillty from oracle support linke – 6880880
copy the zip to ORACLE_HOME.
Remove the existing OPatch directory
Unzip the zip file.
Now check the opatch version
We have installed opatch utility successfully.
Now let’s proceed with PSU patch installation.
INSTALLING PSU PATCH
Copy and unzip the PATCH ZIP FILE:
Check for conflict again ORACLE_HOME.
Shutdown database and listener.
NOTE – If any Goldengate process is running on the ORACLE_HOME, then those all need to be shutdown.
Check for active executables:
Apply the patch:
cd 27734982
$ORACLE_HOME/OPatch/ opatch apply
patching completed. Warnings can be ignored.
Check the inventory, whether the patch has been updated or not:
Start the database and listener.
Run the post-patch script:
compile the invalid object.
Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR

No change on MS Windows
First of all, let me say that there won’t be any changes on the Windows platform. If your preferred operating system is MS Windows then stop reading here. On Windows you’ll see exactly the same patching format with Bundle Patches as you saw before.
How about the other platforms?
Everybody else will see changes with Oracle Database 12.2.0.1 – and I blogged about it a while ago:
As I presented now about the first release model already at a User Group Conference I have had some discussions already about RU and RUR – and I believe there’s a bit more clarification needed.
Differences between PSU/BP and RU/RUR
In July 2017 the first Oracle Database 12.2.0.1 RU became available, since October the second RU and the first RUR are available.
But there’s a significant difference between PSUs and RURs. Even though we say “RURs replace PSUs” RURs are not the same as PSUs.
When you look at the PSU and BP trains before you usually choose at the entry to a release which path you’d like to follow, either PSUs every quarter, or BPs. Engineered system customers had no choice: it was Bundle Patches. In Oracle 11.2. the BPs were meant only for Engineered-systems environments. In Oracle 12.1 we switched and recommended BPs over PSUs for all systems.
Patch Set Updates And Bundle Patches
A Patch Set Update (PSU) contains usually security fixes and regression fixes, i.e. bug fixes.
» data-medium-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_121.png?fit=300%2C113&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_121.png?fit=300%2C113&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_121.png?resize=300%2C113&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»300″ height=»113″ data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
Typical Patch Set Update (PSU) – quarterly
Whereas a Proactive Bundle Patch (BP) was a superset of a PSU containing the PSU but optimizer fixes and functional fixes which may be sometimes feature extensions as well.
» data-medium-file=»https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/bp_121.png?fit=300%2C86&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/bp_121.png?fit=550%2C157&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/bp_121.png?resize=550%2C157&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»550″ height=»157″ srcset=»https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/bp_121.png?w=550&ssl=1 550w, https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/bp_121.png?resize=300%2C86&ssl=1 300w» sizes=»(max-width: 550px) 100vw, 550px» data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
Typical Bundle Patch (BP) – quarterly released
And you choose either one train usually. But you could also change from PSUs to BPs or vice versa. Your flow would actually look like this:
» data-medium-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_bp_121.png?fit=300%2C138&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_bp_121.png?fit=740%2C340&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_bp_121.png?resize=740%2C340&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»740″ height=»340″ srcset=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_bp_121.png?w=800&ssl=1 800w, https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_bp_121.png?resize=300%2C138&ssl=1 300w, https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/psu_bp_121.png?resize=768%2C353&ssl=1 768w» sizes=»(max-width: 740px) 100vw, 740px» data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
Quarterly Patching with either PSUs or BPs – every quarter gets new fixes, PSUs and BPs, each are cumulative to themselves
As PSUs and BPs, each are cumulative you’ll get the fixes from all previous PSUs or BPs for the same release included as well. The PSU a quarter later has new security fixes and new regression fixes added, the Bundle Patch in addition gets new optimizer and functional fixes and of course the same new security and regression fixes the PSU has gotten.
Release Updates
Release Updates (RU) look pretty similar to Bundle Patches (BP):
» data-medium-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122.png?fit=300%2C192&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122.png?fit=301%2C193&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122.png?resize=301%2C193&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»301″ height=»193″ srcset=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122.png?w=301&ssl=1 301w, https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122.png?resize=300%2C192&ssl=1 300w» sizes=»(max-width: 301px) 100vw, 301px» data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
The first Release Update (RU-1)
The following second Release Update contains everything from Release Update 1 plus new fixes in all four areas (marked in dark red/purple below). RUs are cumulative as well as the BPs were.
» data-medium-file=»https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122_2.png?fit=298%2C193&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122_2.png?fit=298%2C193&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ru_122_2.png?resize=298%2C193&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»298″ height=»193″ data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
The second Release Update (RU-2)
RUs get released quarterly at the usual dates.
Release Update Revisions
A Release Update Revision (RUR) is different from an PSU. At the time of the release of RU1 there won’t be an RUR yet. The first RUR will be released containing the entire first RU – plus additional fixes on top. Regression fixes are fixes for misbehavior. They usually hit a lot of customers.
» data-medium-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/rur1.png?fit=300%2C228&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/rur1.png?fit=300%2C228&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i1.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/rur1.png?resize=300%2C228&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»300″ height=»228″ data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
First Release Update Revision (RUR-1)
Actually the first RUR will be released usually a quarter after the first Release Update (RU). It will include all fixes from Release Update 1 (RU-1) – and add only new security and regression fixes on top. But no new optimizer or functional fixes. When you compare it with the picture above (“The second Release Update”) you’ll spot the same security and regression fixes.
At this date you will have the choice now:
3 months later the next RUR will be released – and it will contain now again only the new security and regression fixes (marked in turquoise ) on top. There won’t be any new optimizer or functional fixes added at this point. When you compare both pictures, the one above and the one below (RUR-1 and RUR-2) you’ll see the exact same optimizer and functional fixes from the initial RU-1.
» data-medium-file=»https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/rur2.png?fit=300%2C229&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/rur2.png?fit=300%2C229&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i2.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/rur2.png?resize=300%2C229&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»300″ height=»229″ data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
Second Release Update Revision (RUR-2)
And at the same time the third Release Update (RU-3) will become available as well.
It’s important to mention that there is no third Release Update Revision (RUR-3) planned. The model allows only 2 RURs per RU. Afterwards you have the option to either get the most recent RU – or an RUR based on an older RU.
Overview – The Big Picture
The full picture summarizes the schema:
» data-medium-file=»https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/full_schema_ru_rur.png?fit=300%2C156&ssl=1″ data-large-file=»https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/full_schema_ru_rur.png?fit=740%2C386&ssl=1″ loading=»lazy» src=»https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/full_schema_ru_rur.png?resize=740%2C386&ssl=1″ alt=»Differences between PSU / BP and RU / RUR» width=»740″ height=»386″ srcset=»https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/full_schema_ru_rur.png?w=800&ssl=1 800w, https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/full_schema_ru_rur.png?resize=300%2C156&ssl=1 300w, https://i0.wp.com/mikedietrichde.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/full_schema_ru_rur.png?resize=768%2C400&ssl=1 768w» sizes=»(max-width: 740px) 100vw, 740px» data-recalc-dims=»1″ />
Overview on Release Updates (RU) and Release Update Revisions (RUR) over time
Now you see why there is a significant change. There’s no such thing as PSUs anymore. And you are not nailed on a track. You have the choice to either progressively step forward by applying Release Updates – or pause with new optimizer and functional fixes for up to 6 months patch period.
Related
Does your GI RU/RUR patch level has to match your database’s?
New SPFILE parameters in Oracle Database 12.1.0.2 with July 2016 (and newer) PSU/BP
11.2.0.2 Bundled Patch 3 for Linux x86-64bit released
24 Responses
Many thanks you for clarify. It’s not so easy to understand.
May I ask anything else: what are “Mitigate” patches? I’ve read in conclusion with OJVM patches
Best regards
Peter
I’m trying to understand what is the best way to receive the optimizer fixes with the latest RU/RURs. Even after I apply the latest RU or RUR, the optimizer fixes are disabled by default. How do I know what fixes were included and how do I decide which ones to turn on or leave off. I think there needs to be some clarity around this.
I know that this is a strange topic. But in fact I tried to clarify this more here:
https://mikedietrichde.com/2017/11/07/ru-rur-recommendations-facts/
Please check the RU’s readme. If it DOES NOT contain this paragraph:
“This patch introduces fix control for one or more fixes contained herein. These fixes are disabled by default and will have to be explicitly enabled via alter session/system commands to persist in pfile/spfile as appropriate”
then no BEHAVIOR CHANGING OPTIMIZER fixes are included and thus nothing to switch on. As soon as this paragraph is present in the RU’s readme there will be guidance which _fix_control setting needs to be used in order to enable the fixes.
In the July and October RU for 12.2.0.1 there are no such fixes as far as I can see.
some of the images are missing in this article, could you pls re-publish the page with the images loaded properly
are you sure? I tried different browsers and for me all the pictures get displayed correctly.
Can you please check again and maybe hold the SHIFT key when you push RELOAD in your browser (than it should fetch images again).
I know this is a bit confusing – and another reason why I disrecommend to touch RURs unless you get a clear advice from Support or the MAA/Exadata team.
Let me explain this with months – I think then it is less confusing.
Example:
– in January we release 18.1.0 – no RU or RUR available
– in April we release 18.2.0 – and for the initial release (18.1.0) there won’t be any RUs or RURs
– in July we release 18.3.0 (RU and on-prem base release) and 18.2.1 (RUR-1 on top of 18.2.0)
Both, 18.3.0 and 18.2.1 have the same security and regression fixes. But 18.3.0 has more additional fixes and behavior changing optimizer fixes turned off by default.
– in October we release 18.4.0 (RU), 18.2.2 (final RUR for 18.2.0) and 18.3.1 (first RUR for 18.3.0)
All contain the same security and regression fixes. But they settle on different RUs meaning the amount of fixes is very different
In theory you could switch technically between all 3 of them. But let’s say you give 18.4.0 a try and decide later to roll back to an older patch, you could go backwards to 18.3.1 and 18.2.2 having the same security and regression fixes but missing a lot of additional fixes your release had already consumed. This is technically possible but not recommended.
When I write RU-2 contains the RUR-1 that means that RU-2 has the same fixes as RUR-1 delivers – but more.
This is credited to the fact that RU-2 contains:
– RU-1 ( Differences between regression and functional fixes. says:
Hi Mike,
Thanks for your article.
I would like to know the differences between regression and functional fixes.
I could guess but I’d rather be sure.
My client traditionally applies a patch policy consisting of applying interim patches because he fears bugs caused by Patches (PSUs and BPs before, RUs and RURs now). He would be comfortable applying patches with only security bugs … I think the most similar approach would be applying RU and all the RURs of this RU until the next RU.
I was trying to find the relevant MOS note explaining the differences between regression and functional fixes but was unable to find it.
You client must change the policy. First of all, there are no bundles containing security fixes only. And second, there are no PSUs anymore.
Release Updates are the same as Bundle Patches. And stay away from Revisions unless Oracle Support ask you specifically to apply a Revision – see here, why you (or your client should stay away from it):
https://mikedietrichde.com/2018/11/08/why-release-update-revisions-rur-are-tricky/
Hi Mike,
Thanks for your answer.
In fact, we’re going to propose to our client to apply only RU’s, every six months.
But, it would be useful if I knew clearly the difference between functional and regression fixes.
I think regression fixes fix functionality which used to work in a previous RU or RUR but is broken in a later release RU or RUR
Functional fixes fix code is not working as expected. This code is mostly introduced in the previous release
I tried to find an official definition – but wasn’t successful.
You may try to clarify the terms via an SR please.
Пора. Обновление до Oracle Database 12
Время летит быстро, и для пользователей Oracle Database 11.2, не говоря уже о более ранних версиях, настало время обновления. 31 января 2015 года закончился период Premier Support базы Oracle Database 11.2. Это значит, что если вы, например, запланируете обновление аппаратного сервера, то на нем придется установить новую версию операционной системы, т.к. драйверы для прежней версии уже недоступны, а новая операционная система уже не сертифицирована под версию 11.2.
Детальную информацию о поддержке различных версий Oracle Database вы найдете в официальном документе Oracle Lifetime Support Policy. Только что, например, завершилась расширенная поддержка версии 11.1 (рис. 1). Что касается самой популярной на сегодня версии 11.2 — для нее сейчас заканчивается первый год расширенной поддержки, и с января будущего года начнется постепенное увеличение стоимости технической поддержки, сначала на 10%, в последующие годы — на 20%, и это еще один экономический стимул для предприятий подумать об обновлении до версии до 12с. 
Готовясь к переходу на новую версию базы данных, важно понимать разницу между терминами «обновление» и «миграция».
Обновление (upgrade) базы данных — это переход на новую версию в рамках прежнего операционного окружения — платформа и операционная система не меняются, данные не «переезжают» с одного сервера на другой, меняется только версия базы данных. Собственно обновление заключается в процедуре обновления словаря и метаданных Oracle, сами данные не изменяются и не перемещаются. В этом случае размер базы данных не имеет значения и не влияет на скорость обновления, имеет значение только количество объектов в базе данных. То есть, с обновлением все понятно, меняется только версия базы данных, в данном случае, мы делаем апгрейд до 12 версии базы данных, но платформа и операционная система не меняются.
Важно, с какой именно версии Oracle Database осуществляется обновление на версию 12c. Начиная с версии 10 доступна технология Data Pump. Для обновления со старых версий предусмотрен процесс, состоящий из экспорта и последующего импорта данных, который требует дополнительного дискового пространства. Этот способ часто используют для небольших баз данных. Oracle рекомендует использовать специальный инструмент обновления, который называется Oracle Database Upgrade Assistant и бесплатно поставляется в составе дистрибутива Oracle Database, его применимость к различным версиям баз данных отражена на диаграмме на рис. 2. Начиная с 12 версии доступен также вариант ручного обновления, который обеспечивается виде специальным скриптом на языке Perl.
Можно максимально сократить время простоя при обновлении, если использовать дополнительную возможность, которая появилась в утилите Recovery Manager — сделать перенос файлов в базу данных с помощью транспортируемых табличных пространств, а затем применить инкрементальные копии Recovery Manager. Эта технология называется RMAN incremental backup recovery. Если простой недопустим, нужно использовать специальный инструмент, который обеспечивает обновление «на лету» и называется Golden Gate — но это самый дорогой способ с точки зрения лицензирования ПО, подготовки и адаптации механизмов репликации. 
Миграция (migration) — это переход на новое операционное окружение — на новый сервер, на новую операционную систему. И в этом случае, конечно, имеет первостепенное значение физический размер базы данных. Часто задачи обновления и миграция выполняют совместно, т.е., например, одновременно переходят на новую версию Oracle Database и при этом меняют оборудование.
Самый надежный вариант переноса базы данных прим миграции — старый, добрый экспорт-импорт. Поскольку файл экспорта не зависит от платформы, можно сделать выгрузку из базы данных старой версии на одной программно-аппаратной платформе, а импорт в базу данных новой версии — на другой программно-аппаратной платформе. Начиная с версии 10.2 доступна технология транспортирования табличных пространств. Технология RMAN incremental backup recovery применима, к сожалению, не для всех программно-аппаратных платформ. Если необходим нулевой простой, можно использовать технологию Golden Gate.
Более подробно о способах обновления и миграции вы сможете узнать из документов, перечисленных в конце статьи.
Патчи и сертификация
Если в процессе перехода на новую версию базы данных вы меняете оборудование и операционную систему, нужно разобраться, сертифицирована ли данная программно-аппаратная платформа под версию Oracle Database 12с. Пожалуйста, ознакомьтесь с информацией о сертификации программно-аппаратных платформ, приведенной на сайте технической поддержки support.oracle.com (закладка «Certification»). На том, где искать дистрибутивы, мы останавливаться здесь не будем — важно не забыть получить все актуальные пакеты обновления. Oracle ежеквартально выпускает большие кумулятивные пакеты обновления, которые устраняют серьезные ошибки. Рекомендуемые патчи для версии 12.1.0.2 в настоящий момент — это PSU Update 4 и OJVM PSU Update 4 (обновление Oracle Java Virtual Machine, встроенной машины Java).
Если сейчас вы используете версию 11.2.0.3 или 11.2.0.4, и уже установили определенные патчи для устранения определенных ошибок, стоит убедиться, что эти ошибки исправлены в версии 12. Скорее всего, это так, но, тем не менее, рекомендуется по номеру патча к версии 11 проверить, устранена ли специфическая ошибка в кумулятивном обновлении версии 12, и если нет, то получить соответствующую «заплатку» для устранения данной ошибки. Если же такой патч еще не выпущен, необходимо сделать соответствующий запрос в службу технической поддержки для вашей программно-аппаратной платформы.
Начиная с версии 12.1.0.2 Oracle выпускает специальный патч, который называется Oracle Database In-Memory patch of Exadata Engineering System. Он включает обновление технологии Oracle Database In-Memory и, несмотря на свое название, подходит не только к Exadata, но и к обычным дистрибутивам, и который рекомендуется устанавливать, если вы используете технологию Oracle Database In-Memory.
Важное обновление касается особенностей измерения времени в России — это связано с тем, что у нас, как вы помните, был дважды с интервалом в несколько лет изменен принцип исчисления времени в часовых поясах. Поэтому очень важно установить специальные Time Zone-обновления, которые учитывают эту ситуацию для российских часовых поясов. Если вы активно используете хранимые процедуры на Java и переменные Java типа Date и Time с часовыми поясами, вам пригодится специальный патч для коррекции времени в часовых поясах для виртуальной машины Java.
Не забудьте обновить утилиту OPatch для того, чтобы установить новое обновление. В Oracle Database 12 версии появился новый пакет DMBS_QOPatch.
Подготовка исходной базы данных
Прежде чем начать обновление, нужно подготовить исходную базу данных. «Чеклист» такой подготовки приведен на рис. 3. 
Очистка мусорной корзины перед обновлением. Начиная с Oracle 12с она выполняется с помощью скрипта preupgrade_fixups.sql. Очищать мусорную корзину рекомендуется, по меньшей мере, раз в неделю с помощью автоматического задания в период минимальной нагрузки на базу данных.
Проверка на ошибочные объекты. Не должно быть ошибочных объектов в схемах SYS и SYSTEM. Чтобы произвести такую проверку, нужно попытаться скомпилировать объекты, находящиеся в состоянии «Invalid», до обновления или миграции с помощью скрипта utlrp.sql. Если это не помогает, приступать к обновлению ни в коем случае нельзя. Стоит проверить, нет ли в схемах SYS и SYSTEM объектов с одинаковыми именами, это можно сделать при помощи следующего запроса:
Также удалите все устаревшие и недокументированные параметры, включая events. Если вы работаете с большими, сложными приложениями, такими как ERP SAP или Oracle EBS, обязательно ознакомьтесь с приложенной к ним документацией об обновлении базы данных для таких приложений. Есть пример обновления базы данных самой компании Oracle — когда удалили все недокументированные параметры, скорость обновления увеличилось в семь раз.
Существует прекрасная утилита Health Check — это скрипт, который позволяет проверить целостность словаря. Этот скрипт проверяет известные проблемы в Oracle8i, Oracle9i, Oracle 10g и Oracle 11g. Для более высокой производительности его может запустить в несколько параллельных каналов или только для отдельных файлов данных или табличных пространств. Health Check выполняется на базе данных и выводит в консоль SQL+ информацию по всем компонентам. Если будет обнаружена несогласованность словаря, скрипт выведет эту информацию, а вам придется решить эту проблему перед обновлением, потому что словарь должен быть в согласованном состоянии. Скачать утилиту можно с сайта службы технической поддержки.
Также в версии 12 появился новый специальный Pre-Upgrade-скрипт preupgrd.sql. Он выполняет проверки перед обновлением, запускается в базе данных старой версии и выполняет проверки окружения старой базы данных на соответствие перехода на версию 12. Если обнаруживаются какие-то несоответствия, то формируются два специальных скрипта: preupgrade_fixups.sql и postupgrade_fixups.sql.
Для увеличения скорости обновления рекомендуется иметь актуальную статистику — прежде всего, статистику по метаданным СУБД Oracle. Сбор статистики по словарю осуществляется с помощью вызова пакета DBMS_STATS, GATHER_DICTIONARY_STATS. Актуальной может считаться статистика, собранная не более чем за сутки до обновления.
Обновление базы данных
Теперь мы можем приступить к самой процедуре обновления. Продолжительность обновления до Oracle Database 12с в основном зависит от количества компонентов, опций и объектов в базе данных — поскольку в версии 12 появилось много новых таблиц и была реорганизована структура базовых таблиц. В меньшей степени продолжительность обновления зависит от производительности системы, т.е. частоты и количества центральных процессоров и скорости подсистем ввода-вывода. В версии 12 обновление словаря происходит в параллельном режиме — по умолчанию в четыре потока. К сожалению, максимальная степень параллелизма ограничена значением 8 — т.е. можно создать максимум восемь потоков, поскольку словарь имеет максимум восемь независимых компонентов, которые можно обновлять параллельно. Возможно, в будущих версиях степень параллелизма будет повышена. Впрочем, уже теперь документация обещает 40%-ное повышение скорости обновления словаря, а опыт заказчиков показывает, что возможна и более высокая скорость.
Упрощает обновление до Oracle Database 12c инструмент администрирования Database Upgrade Assistant, который входит в дистрибутив СУБД Oracle и не требует дополнительного лицензирования. Можно вызвать его через общую консоль Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, это удобно, если необходимо провести массовое обновление баз данных однотипной конфигурации. Если нужно обновить кластерную базу данных, можно использовать консоль Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
Завершение обновления
Чтобы выполнить набор шагов для завершения обновления, следует воспользоваться специальным скриптом, который называется utlu121s.sql, или утилитой Database Upgrade Assistant. Скрипт выводит перечень компонентов базы данных — статус каждого компонента статус должен быть VALID, в противном случае обновление прошло неудачно. Отдельно следует проверить результат установки специальных обновлений Time Zone — бинарных патчи определения часовых поясов и специальный скрипт, который производит изменение словаря. 
На рис. 4 приведен проверочный список для проверки производительности обновленной базы данных. Можно использовать технологию Real Application Testing, которая позволяет записать нагрузку на базе данных старой версии, проиграть ее на базе данных новой версии и сравнить производительность.