non manifold geometry что это
Теория полигонального 3D-моделирования в Maya
В этой статье Jahirul Amin рассмотрит основные составляющие теории полигонального моделирования.
Квады против трисов и N-гонов
Итак, какая же разница между квадом, трисом и N-гоном? Ну, квад – это полигон, у которого 4 стороны, трис – это полигон, у которого 3 стороны, N-гон – это полигон, у которого больше 4 сторон.
В процессе моделирования лучше всего придерживаться четырехугольников или квадов. Главным образом из-за того, что дивайдятся они более предсказуемо, лучше деформируются в анимации, а текстуры искажаются меньше всего.
Трисы или треугольники лучше всего использовать там, где их меньше всего видно.
А вот использования N-гонов лучше вообще избегать, поскольку на рендере они могут образовывать странные артефакты, а хорошо раскрасить скин с многоугольниками при риге вообще практически невозможно.
Кроме того, в программах для цифрового скалптинга, таких, как ZBrush and Mudbox удобнее всего работать с моделью, состоящей из четырехгольников.
Радость от полигонов и печаль от многоугольников
Uniform-геометрия
Uniform-геометрия значит, что в процессе моделирования вы стараетесь максимально придерживаться четырехугольников или квадов, размещая их максимально равномерно. Делать риг такой геометрии будет одно удовольствие, она будет отлично деформироваться на анимации. И, несмотря на то, что хорошие текстуры во многом зависят от хорошей UV-развертки, искажаться они будут еще меньше, если геометрия будет состоять из четырехугольников.
В Maya есть прекрасный инструмент Sculpt Geometry, с помощью которого, при условии перехода в режим Relax, можно прекрасно сгладить эджи по краям.
С помощью инструмента Sculpt Geometry можно сгладить эджи
На первый взгляд расположение эджей не имеет никакого значения. Но это не так.
При моделировании реалистичных персонажей стоит изучить анатомию человека. В таком случае направление эджей и топология должны соответствовать расположению мышц на теле человека, что создаст более правильную деформацию геометрии.
В случае с более мультяшными и стилизованными персонажами пространства для маневра больше, однако, знание анатомии лишним не будет даже в этом случае.
Для корректных деформаций топология должна быть соответствующей с необходимыми эдж лупами
Non-manifold-геометрия
Non-manifold-геометрия может содержать различные ошибки, возникшие в процессе моделирования. Это могут быть висящие эджи (без фейсов); эджи, общие для трех и более фейсов; нормали соседних фейсов, направленные в противоположные стороны; число фейсов, сходящихся в одной вершине может отличаться от числа фейслов, исходящих из этой вершины и пр.
Например, создайте куб, выделите один из его эджей и выполните команду Edit Mesh > Extrude. Итак, мы получили non-manifold-объект. Если бы это был лист бумаги, то это был бы сгиб, от которого было бы сложно избавиться. Если выполнить операцию Boolean для такого куба, то все сразу же станет понятным.
Non-manifold-геометрия может доставить немало боли, поэтому старайтесь избегать ее. Инструмент Cleanup, который находится в меню Mesh, поможет решить многие проблемы, связанные с non-manifold-геометрией.
Non-manifold-геометрия может доставить много боли
Каждый эдж должен быть на своем месте
В идеале мы начинаем процесс моделирования с простого примитива, например, куба, которому затем добавляем эдж лупы, экструдим и пр.
При этом важно соблюдать простую сложность, добавляя детали только там, где это действительно нужно. Меньше может быть лучше. Со временем вы будете лучше понимать, как оптимизировать модель, а сейчас просто продолжайте моделить.
Не делайте модель излишне сложной, добавляйте детали только там, где это действительно нужно
Изучайте окружающий мир
Все, что мы пытаемся воссоздать программно является отражением реально существующих вещей. Поэтому самым важным советом станет изучение окружающего мира.
И это касается не только моделлеров, но и риггеров, аниматоров, художников по свету и пр. Задумайтесь, как устроен тот или иной объект, как он освещается, деформируется и пр. Поиск ответов на такие вопросы значительно облегчит жизнь.
Читайте в нашей предыдущей статье введение в риг от Jahirul Amin.
What is non-manifold geometry?
I am not quite sure what non-manifold geometry is. I thought non-manifold geometry was just floating vertices and hole in a mesh. From my experience this is not always the case however. What is non-manifold geometry and what are the types of it and how do I avoid it? Is there a case where it is acceptable?
5 Answers 5
Non-manifold geometry is essentially geometry which cannot exist in the real world (which is why it’s important to have manifold meshes for 3D printing).
As JulianHzg points out in the comments, intersecting geometry (faces sticking through other faces) is not technically non-manifold geometry on it’s own. However it will often cause the same issues as non-manifold geometry, i.e. confused volume calculations.
Non-manifold geometry can be problematic, because it complicates some tools & operations:
Rendering of refractive effects
Among many other cases.
You might want non-manifold geometry in some kind abstract model (as non-manifold geometry cannot exist in the real world), or as an approximation of a very thin object (e.g. paper, leaves, etc.)
Common causes of non-manifold geometry:
Disconnected vertices and edges:
Areas with no thickness:
Fixing non-manifold geometry:
Internal faces can be selected by pressing 3D view > Header > Select > Internal Faces in edit mode.
Loose geometry (elements without any other connecting elements) can be selected with 3D view > Header > Select > Loose geometry. Note that it only selects vertices, edges, and faces depending on the current selection mode.
Other useful tools for repairing non-manifold geometry:
Shift G (Select Similar). This is often useful to select vertices with only one connecting edge, etc.
Ctrl L (Select Linked). This is often useful in combination with Select loose and Select similar to select all geometry connected to the selected geometry.
W > Specials > Remove doubles Doubles, (multiple vertices in the same place) are usually non-manifold (not always).
Since a common cause of non-manifold geometry is lack of thickness, the solidify modifier can also be useful.
How To Find Non Manifold Areas in a Mesh
Overlapping Edges
One type of non manifold situation is when you have overlapping edges.
For example, I’d frequently have a mesh that’d look fine, like this:
But then when I checked for non manifolds, I would get an edge highlighted like this:
I discovered the reason this edge was highlighted was because there were overlapping edges.
The way to find the overlapping edges is to grab one of the middle vertices in the highlighted area (circled in green), drag it around and see if you discover a hidden edge, like the white one here:
Once you find that edge, delete it, then put the dragged vertex back into place. One trick I discovered about how to put the vertex back into place easily is when you are first dragging it out out of place, only drag it on one axis, rather than freely in 3, because then you only have to snap it back to that one axis, rather than 3.
When Non-Manifold Geometry is Useful or OK
Ok, I haven’t found any uses for interior faces or overlapping edges, but I find open ended meshes and intersecting («sunken») sub-meshes to be useful in some situations, provided you are:
This is probably mostly useful for lowpoly modelers, though I use it with solid subsurf stuff sometimes as well. Here is a device I’ve been working on for a modding project:
It’s made up of several mesh object. The front iPhone-colored-specular-map-showing one is protruding into the rear cargo unit so that no gaps are visible. If we hide the back one with the hatches, we can see:
There isn’t actually a inside-rear to this part. Also you can see that the sidelights also have open edges sticking into the head mesh, and that the grate-things are protruding into the head a little too despite being closed objects. In this case, users probably aren’t going to be able to get close enough to the object that modelling any more detailed connections between things would be meaningful.
One more thing to note about open edges like this: you can actually loop select them. If you were to fill the hidden area with an N-gon or an efficient triangle spread, you wouldn’t be able to loop select anymore, which I find kind of annoying.
Debatable Cases
When making environmental static meshes for games and such, some designers go for designs like this to save polygons:
(In these examples, presume that the giant yellow UV map is some ugly/error texture that the users are hopefully never to see, and the other three colors are proper textures)
The problem with this design, is that each tiny error in meshing by the map designers can cause a huge immersion-breaking mess for the users:
From my experience wandering artificial environments, these errors, like software bugs, are not so much a ‘if’ as a ‘how many, how bad, and where’ situation.
It does cost some extra polygons, but I find I much prefer making a backing hull for this kind of mesh:
In this case, after extruding the top and bottom edges and creating the rear face, I created an N-gon in each side loop and then triangulated it for a minimal fill. I unwrapped the UVs on these faces and shrunk them to a tiny dark spot in the corner of the map. If I were making lightmaps, I’d try to minimize all these faces to a combined pixel or so as well.
The result when looking at the messed up seam:
I find the pretense of solid mass here much less immersion breaking, even though the unintended faces are minimally texture. Even when you look dead on through the gap:
You can barely even see the ‘bad texture’ texture.
The question is not well stated. There is nothing like non-manifold geometry. Non-manifoldness is a topological property and when we come to computers non-manifoldness is a combinatorial property.
Given a bunch of triangles you can build a manifold or a non-manifold stitching together edges in different ways. Manifoldness of what comes out do not depends of the shape of triangles you use. You can end up in a nightmare of self intersecting triangles but this can not be considered strictly related to non-manifoldness. You can choose other vertexes or you can let yourself float out of 3D to a nD space and all intersections can go away, pushing n high enough. Nevertheless if you stitch a segment to a triangle vertex the broomstick you get is a non-manifold even if you can see all the dimensions of the String Theory.
Defining non-manifoldness could be surprisingly daunting. Manifoldness is a black night in which all the cows are black. Recognizing manifold cows is obvious for triangulated meshes (a.k.a. 2-complexes) and tetrahedralization (3-complexes) but recognizing if a n-complex is a manifold, in general, cannot be done for n greather than six (let alone the String Theory. ). That has something to do with the Halting Problem.
So, all manifolds are equal but some are more equal. There are Pseudomanifolds, Lienhardt’s Quasi Manifolds and Initial Quasi Manifolds, the latter being something that you cannot decide easily how to decompose into parts. There is a linear time algorithm for a non-preemptive decompositon of a non-manifold into Initial Quasi Manifolds.
What hell do I mean for a non-premptive decomposition? Take this tetrahedralization 

However if you consider this as a tetrahedralization you have several options to decompose but none is more equal than the others. You can take this four component decomposition 
So in the end non-manifoldness is a combinatorial property that depends on how I stitch together things. If I am not careful at the way I stitch together things I end up in a non-manifold. However, looking at a non-manifold it is not always possible to tell which was the wrong stitching. Sometimes you (or an AI system) look at the 3D non-manifold object and see its assembly, sometimes you can’t.
It’s not so tricky to define non-manifold in the context of Blender. Non-manifold is what shows up when you use the select non manifold operation.
Non-manifold is better defined by instead defining what «manifold» means:
Non-manifold meshes are just meshes for which one or more of those characteristics is not true.
If we use the select non manifold operation, we can see that there are multiple options for this. Note that the «extend» option is not actually a non-manifold characteristic, but just means to add the selection to our old selection, so we’ll ignore that. Let’s go through the other options to demonstrate:
Is non-manifold geometry ever acceptable? Absolutely, yes! This is visual art. Everything is permitted! Non-manifold geometry is acceptable. But if you want to use non-manifold geometry, you’ll want to know that you’re using it. (And, for most rendering meshes, you probably won’t want to use non-manifold geometry.)
The biggest issue with non-manifold geometry is how it affects your normals. That’s particularly true with smooth-shaded normals, which are interpolated across your faces from vertex normals; and vertex normals are calculated from the face normals of the faces they form. If those faces switch normals, consider that we’re interpolating from a negative normal to a positive normal. That creates a line of singularity of zero normals (or infinity normals), although our samples aren’t likely to see it. It also affects our lighting across the entire face.
Normals are also used by many operations— booleans, physics, more— to determine what’s the inside of the mesh and what’s the outside. For example, the difference between a cave and a rock is simply which direction the normals are pointing. When we have non-manifold geometry, there is no clear inside or outside to the mesh, and these operations are going to fail, or act in unexpected ways.
There are also plenty of operations we can do that are built around an expectation of manifold geometry. Catmull clark subdivision is likely to do what we want with manifold geometry; it is not likely to do what we want with non-manifold geometry.
However, there are some clear cases where non-manifold geometry is not only acceptable, but ideal!
Thin meshes— meshes that fail the «boundary» condition— are routinely used in 3D rendering. Think of hair cards as an example. The fact that these meshes do not have a clear inside or outside doesn’t matter, because we’re not doing anything with them that needs a volume defined. The fact that their normals aren’t defined by a full complement of faces doesn’t matter, because the normals are consistent— and besides, if we wanted, we could give them custom normals, or use a normal map.
Non-rendering meshes are also routinely non-manifold. The easiest way to make a bone that can have only a few specific, arbitrary positions is to shrinkwrap it, nearest vert, to a mesh composed only of verts. Soft body physics meshes routinely have loose edges so that we can create and control forces to affect their operation (and then mesh deform a rendering mesh from these physics meshes.)
And if we’re making an emission mesh, then its normals don’t affect rendering, and we can make a mesh that violates contiguous or multiple faces conditions and just not worry about it, even though those are the conditions that we are usually most concerned with.
Note also that just because non-manifold geometry causes rendering artifacts, that doesn’t mean that all geometry that causes rendering artifacts is non-manifold. A degenerate quad (with three collinear verts, or joining another quad by two of its edges) is just as bad news as multiple faces for smooth shaded normals, but it is not non-manifold geometry. Understanding what non-manifold means, and why to avoid it (or why not to!) is an important part of understanding how to create good topology, but it is not the only part.
Two-manifold and non-manifold polygonal geometry
Polygonal geometry can have different configurations or topology types in Maya. Understanding the characteristics of these topologies can be helpful when you need to understand why a modeling operation failed to execute as expected.
Two-manifold topology polygons have a mesh that can be split along its various edges and unfolded so that the mesh lays flat without overlapping pieces.
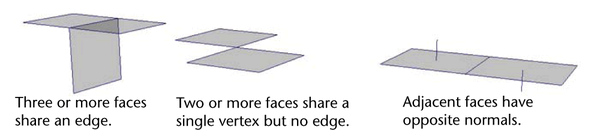
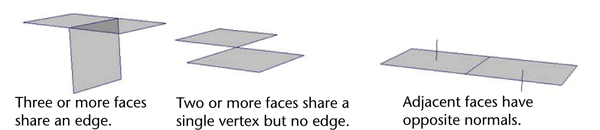
Non-manifold topology polygons have a configuration that cannot be unfolded into a continuous flat piece. Some tools and actions in Maya cannot work properly with non-manifold geometry. For example, the legacy Boolean algorithm, the Reduce feature, and Sculpting Tools do not work with non-manifold polygon topology. The image below shows three examples of non-manifold topology polygons.
This shape is also possible where two three-dimensional shapes share a vertex (such as two cubes meeting at a single point).
The following operations in Maya can produce non-manifold geometry:
Invalid polygon geometry
Some types of polygon geometry will not work in Maya. Invalid geometry includes vertices that are not associated with a polygon edge and polygon edges that are not part of a face (dangling edges). While Maya does not let you create these types of geometry, it may be possible to import these types from other software applications.
Maya LT
Could not retrieve table of contents
Two-manifold vs. non-manifold polygonal geometry
Polygonal geometry can have different configurations or topology types in Maya. Understanding the characteristics of these topologies can be helpful when you need to understand why a modeling operation failed to execute as expected.
Two-manifold topology polygons have a configuration such that the polygon mesh can be split along its various edges and subsequently unfolded so that the mesh lays flat without overlapping pieces.
Non-manifold topology polygons have a configuration that cannot be unfolded into a continuous flat piece. Some tools and actions in Maya cannot work properly with non-manifold geometry. For example, the legacy Boolean algorithm and the Reduce feature do not work with non-manifold polygon topology. The image below shows three examples of non-manifold topology polygons.
This shape is also possible where two three-dimensional shapes share a vertex (such as two cubes meeting at a single point).
The following operations in Maya can produce nonmanifold geometry:
You can convert non-manifold topology polygons into two-manifold topology (including the less obvious case of adjacent faces with opposite normals) using Mesh > Cleanup.
Invalid polygon geometry
Some types of polygon geometry will not work in Maya. Invalid geometry includes vertices that are not associated with a polygon edge and polygon edges that are not part of a face (dangling edges). While Maya does not let you create these types of geometry, it may be possible to import these types from other software applications.
Словарь¶
На этой странице перечислены определения терминов, используемых в Blender и настоящем руководстве.
Action Safe (Зона действия)
Область экрана, видимая на большинстве устройств. Размещайте содержимое внутри неё, чтобы быть уверенным, что оно не будет обрезано.
When many items are selected, the last selected item will be the active one. Used in situations where the interface only shows options for one item at a time.
Артефакты визуализации в виде зазубренных линий.
Alpha Channel (Альфа-канал)
Дополнительный канал в изображении, представляющий его прозрачность.
Straight Alpha (Чистый альфа-канал)
Premultiplied Alpha (Альфа-канал с предумножением)
Это естественный вывод движков визуализации, в которых RGB-каналы представляют количество света, пришедшего к наблюдателю, а альфа-канал представляет, сколько было заблокировано света от фона. Этот тип альфы используется в формате файлов OpenEXR. Таким образом, промежуточные файлы для визуализации и композитинга часто сохраняются с предварительно умноженной альфой.
Преобразование между альфа-каналом с предумножением и чистым альфа-каналом
Conversion between the two alpha types is not a simple operation and can involve data loss, as both alpha types can represent data that the other cannot, though it is often subtle.
Straight alpha can be considered to be an RGB color image with a separate alpha mask. In areas where this mask is fully transparent, there can still be colors in the RGB channels. On conversion to premultiplied alpha, this mask is applied and the colors in such areas become black and are lost.
С другой стороны, альфа-канал с предумножением может представлять визуализации, которые как излучают свет, так и пропускают свет от фона. Например, при визуализации прозрачный огонь может испускать свет, но также позволяет проходить свету от объектов позади него. При преобразовании в чистый альфа-канал этот эффект потеряется.
A separate image map is stored for each color and alpha channel. Channel packing is commonly used by game engines to save memory and to optimize memory access.
Ambient Light (Окружающий свет)
Свет, приходящий из окружающей среды со всех сторон.
A ratio of how much Ambient Light a surface point would be likely to receive. If a surface point is under a foot or table, it will end up much darker than the top of someone’s head or the tabletop.
A reference line which defines coordinates along one cardinal direction in n-dimensional space.
Axis Angle (Осевой угол)
Метод вращения, в котором компоненты X, Y и Z определяют ось, а компонента W соответствует углу поворота вокруг данной оси, в радианах.
Процесс вычисления и сохранения результата потенциально затратных по времени вычислений, чтобы избежать необходимости в таких вычислениях в будущем.
Операция скашивания (делания фасок) рёбер объекта.
Метод в компьютерной графике для генерации и представления кривых.
The exponent value (with base two) for how many colors can be represented within a single color channel. A higher bit depth will allow more possible colors, reducing banding, and increasing precision. Yet a higher bit depth will increase memory usage exponentially.
Blend Modes (Режимы смешивания) Color Blend Modes (Режимы смешивания цветов)
Правила смешивания вместе двух цветов.
Также смотрите статью Blend Modes в документации к GIMP (Режимы слоя на русском языке).
Тип логики, имеющий дело с двоичными состояниями да/нет.
Bounding Box (Ограничительная рамка)
Рамка, в которую заключена форма объекта. Эта рамка выравнивается по осям локального пространства объекта.
Bump Mapping (Наложение рельефа)
Technique for simulating slight variations in surface height using a grayscale «heightmap» texture.
BVH Bounding Volume Hierarchy (Иерархия ограничивающего объёма)
Иерархическая структура геометрических объектов.
Также смотрите статью Bounding Volume Hierarchy на англоязычной Википедии.
The optical phenomenon of light concentration focused by specular reflections or refracting objects. In example observable on light passing through a glass of water onto a table or the pattern at the bottom of a swimming pool.
In rendering this refers to diffuse reflected light paths after a glossy or refraction bounce.
See also Caustics on Wikipedia.
Chroma (Насыщенность цвета) Chrominance (Цветоразность)
В общем случае, декомпозиция цвета результирующего изображения, в котором отдельно выделяется канал яркости (L или Y). Этот термин используется в двух различных контекстах:
Относится к разложению цвета в общем случае на каналы Y (Яркости) и C (Цветности), в этом случае цветоразность представляется как: U = (Синий минус Яркость) и V = (Красный минус Яркость).
Refers to a point in the color gamut surrounded by a mixture of a determined spectrum of its RGB neighboring colors. This point is called Chroma key and this key (a chosen color) is used to create an Alpha Mask. The total amount of gamut space for this chrominance point is defined by users in a circular or square-shaped format.
The coordinates of the Primaries on the CIE 1931 xy chromaticity diagram.
Clamp (С ограничением) Clamping (Отсечение)
Limits a variable to a range. The values over or under the range are set to the constant values of the range’s minimum or maximum.
Color Gamut (Цветовой гамут)
Гамутом традиционно называют объём цветов, представимых в определённой цветовой модели. Во многих случаях он часто представляется в виде двумерного графика в координатах CIE Yxy.
Color Space (Цветовое пространство)
Система координат, в которой вектора представляют значения цвета. Таким образом, цветовое пространство определяет три вещи:
The exact color of each of the Primaries
Три значения, часто рассматриваемые как более интуитивная (по человеческому восприятию) система, чем RGB.
Also known as colorfulness, saturation is the quantity of hue in the color (from desaturated – a shade of gray – to saturated – brighter colors).
Яркость цвета (от тёмного к светлому).
HSL Hue, Saturation (Тон, Насыщенность)
Стандарт яркости-цветности, используемый в аналоговом широковещательном PAL-видео (в Европе).
Компонентное видео Яркость-КаналСинего-КаналКрасного для использования в цифровом вещании, чьи стандарты были обновлены для HDTV. Обычно его называют форматом HDMI для компонентного видео.
Concave Face (Вогнутая грань)
Грань, у которой одна вершина находится внутри треугольника, формируемого другими вершинами грани.
A way of controlling one Object with data from another.
Convex Face (Выпуклая грань)
Относится к любому набору элементов, которые лежат в одной плоскости в трёхмерном пространстве.
An existing Blender object, which is using its own data, or linked data (data owned and controlled by another Blender object).
Diffuse Light (Диффузный свет, рассеянный свет)
Разнонаправленный свет, исходящий от поверхности. Для большинства вещей рассеянное освещение является основным видимым нами освещением. Рассеянный свет приходит с конкретного направления или из конкретного местоположения и создаёт затенение. Поверхности, направленные в сторону источника света, будет ярче, а поверхности, направленные от источника света – темнее.
Directional Light (Направленный свет)
The light that has a specific direction, but no location. It seems to come from an infinitely far away source, like the sun. Surfaces facing the light are illuminated more than surfaces facing away, but their location does not matter. A directional light illuminates all objects in the scene, no matter where they are.
Displacement Mapping (Карта смещений)
Display Referenced (Представимое на дисплее)
DOF Depth of Field
Расстояние, на котором любой объект находится в фокусе. Для любых настроек объектива существует только одно расстояние, на котором объект находится точно в фокусе, но поскольку фокусировка по обе стороны от этого расстояния спадает постепенно, регион гдубины резкости размывается не так сильно, как области за пределом этого региона. Уровень размытия в регионе больше за точкой фокуса, нежели перед ней, поскольку световые лучи быстрее меняют свой угол расхождения; чем дальше расстояние от камеры, тем больше они становятся параллельными.
Double Buffer (Двойная буферизация)
Technique for rendering and displaying content on the screen. Blender uses two buffers (images) to render the interface, the content of one buffer is displayed while rendering occurs on the other buffer. When rendering is complete, the buffers are switched.
Edge Loop (Петля рёбер)
Edge Ring (Кольцо рёбер)
Path of all Edges along a Face Loop that share two faces belonging to that loop.
Objects that are able to spontaneously return to their original shape after all outside forces are removed from the object.
The amount a material is elastic versus inelastic.
Euler (Эйлер) Euler Rotation (Вращение Эйлера)
Rotation method where rotations are applied to each of the X, Y, Z axes in a specific order.
Euler orders in Blender are most intuitive when read backwards: XYZ Euler is similar to rotating around Local Z using the Rotate tool in the 3D Viewport, followed by Local Y and then Local X.
Кривая, хранящая значения анимации определённого свойства.
Face Loop (Петля граней)
Face Normal (Нормаль к грани)
The normalized vector perpendicular to the plane that a Face lies in. Each face has its own normal.
Field of View (Поле зрения)
Rendering artifacts encountered with path tracing resulting from improbable samples that contribute very high values to pixels.
FK Forward Kinematics
The process of determining the movement of interconnected segments or bones of a body or model in the order from the parent bones to the child bones. Using forward kinematics on a hierarchically structured object, you can move the upper arm then the lower arm and hand go along with the movement. Without forward kinematics the lower arm and hand would disconnect from upper arm and would move independently in space.
Focal Length (Фокусное расстояние)
In video compression, a frame can be compressed by several different algorithms. These algorithms are known as picture types or frame types and there are three major types: I, P, and B frames.
The least compressible but don’t require other video frames to decode.
Use data from previous frames to decompress and are more compressible than I‑frames.
Use both previous and forward frames for data reference to get the highest amount of compression.
Операция, используемая для регулировки яркости изображения.
Также смотрите статью Gamma correction на англоязычной Википедии и статью Гамма-коррекция на русскоязычной Википедии.
Geometric Center (Геометрический центр)
Среднее арифметиеское позиций всех вершин, составляющих объект.
Поворотный механизм, позволяющий объекту вращаться вокруг одной оси.
Также смотрите статью Gimbal на англоязычной Википедии и статью Карданов подвес на русскоязычной Википедии.
Gimbal Lock (Шарнирный клин)
The limitation where axes of rotation can become aligned, losing the ability to rotate on an axis (typically associated with Euler Rotation ).
Также смотрите статью Gimbal lock на англоязычной Википедии и статью Складывание рамок на русскоязычной Википедии.
See also Gimbal lock on Stack Exchange.
Global Illumination (Глобальное освещение)
A superset of Radiosity and ray tracing. The goal is to compute all possible light interactions in a given scene, and thus, obtain a truly photorealistic image. All combinations of diffuse and specular reflections and transmissions must be accounted for. Effects such as color bleeding and caustics must be included in a global illumination simulation.
Global Space (Глобальное пространство)
Glossy Map (Карта глянца)
HDRI High Dynamic Range Image (Изображение в высоком динамическом диапазоне)
Набор методов, которые позволяют использовать намного больший динамический диапазон воздействий, нежели обычные методы цифровой обработки изображений. Идея состоит в том, чтобы точно представлять широкий диапазон уровней интенсивностей в реальных сценах, начиная от освещения прямыми солнечными лучами и заканчивая самыми глубокими тенями.
Также смотрите статью High Dynamic Range Image на англоязычной Википедии и статью High Dynamic Range Image на русскоязычной Википедии.
IK Inverse Kinematics (Инверсная кинематика)
The process of determining the movement of interconnected segments or bones of a body or model in the order from the child bones to the parent bones. Using inverse kinematics on a hierarchically structured object, you can move the hand then the upper and lower arm will automatically follow that movement. Without inverse kinematics the hand would come off the model and would move independently in space.
IOR Index of Refraction
Свойство прозрачных материалов. Когда луч света путешествует через один и тот же объём, он идёт по прямому пути. Однако, если он переходит из одного прозрачного объёма в другой, он отклоняется. Угол, на который отклонился луч, может быть определён из показателей преломлений материалов обеих объёмов.
Keyframe (Ключевой кадр)
A frame in an animated sequence drawn or otherwise constructed directly by the animator. In classical animation, when all frames were drawn by animators, the senior artist would draw these frames, leaving the «in between» frames to an apprentice. Now, the animator creates only the first and last frames of a simple sequence (keyframes); the computer fills in the gap.
Keyframing (Создание ключевых кадров)
Вставка ключевых кадров для построения анимированной последовательности.
Тип объекта, состоящий из невизуализируемой трёхмерной сетки вершин.
Light Bounces (Отскоки света)
Local Space (Локальное пространство)
Интенсивность источника света либо в канале изображения/модели, либо испущенного с единицы поверхности в заданном направлении.
Manifold meshes, also called water-tight meshes, define a closed non-self-intersecting volume (see also Non-manifold ). A manifold mesh is a mesh in which the structure of the connected faces in a closed volume will always point the normals (and there surfaces) to the outside or to the inside of the mesh without any overlaps. If you recalculate those normals, they will always point at a predictable direction (To the outside or to the inside of the volume). When working with non-closed volumes, a manifold mesh is a mesh in which the normals will always define two different and non-consecutive surfaces. A manifold mesh will always define an even number of non-overlapped surfaces.
Stands for «material capture», using an image to represent a complete material including lighting and reflections.
Matte (Маска) Mask (Маска)
Полигоны размером с пиксель или даже меньше.
MIP Mip-map Mip-mapping
MIS Multiple Importance Sampling
A process of estimating the direction of light rays to improve sampling quality.
A non-destructive operation that is applied on top of some sort of data.
Motion Blur (Размытие при движении)
Явление, возникающее, когда мы воспринимаем быстро движущийся объект. Объект представляется размытым из-за нашей инерции зрения. Имитация размытия при движении делает компьютерную анимацию более реалистичной.
Non-Manifold meshes essentially define geometry which cannot exist in the real world. This kind of geometry is not suitable for several types of operations, especially those where knowing the volume (inside/outside) of the object is important (refraction, fluids, Boolean operations, or 3D printing, to name a few). A non-manifold mesh is a mesh in which the structure of a non-overlapped surface (based on its connected faces) will not determine the inside or the outside of a volume based on its normals, defining a single surface for both sides, but ended with flipped normals. When working with non-closed volumes, a non-manifold mesh will always determine at least one discontinuity in the normal directions, either by an inversion of a connected loop, or by an odd number of surfaces. A non-manifold mesh will always define an odd number of surfaces.
Существует несколько типов неразвёртываемой геометрии:
Некоторые границы и дырки (рёбра с только одной связанной гранью), когда грани не имеют толщины.
Рёбра и вершины, не принадлежащие ни к одной грани (каркас).
Рёбра, соединённые с тремя или более гранями (внутренние грани).
Вершины, принадлежащие к не соседним граням (к примеру, два конуса имеют общую вершину на верхушке).
Animation technique that allows the animator to edit motions as a whole, not just the individual keys. Nonlinear animation allows you to combine, mix, and blend different motions to create entirely new animations.
Нормализованный вектор, перпендикулярный к поверхности.
See also Normals on Wikipedia.
Normal Mapping (Карты нормалей)
NURBS Non-uniform Rational Basis Spline (Неоднородный рациональный базовый сплайн)
Метод в компьютерной графике для генерации и представления кривых и поверхностей.
Container for a type (mesh, curve, surface, metaball, text, armature, lattice, empty, camera, light) and basic 3D transform data ( Object Origin ).
Object Center (Центр объекта) Object Origin (Опорная точка объекта)
The graphics system used by Blender (and many other graphics applications) for rendering 3D graphics, often taking advantage of hardware acceleration.
Также смотрите статью OpenGL на англоязычной Википедии и статью OpenGL на русскоязычной Википедии.
Overscan (Вылет развёртки)
Термин, используемый для описания ситуации, когда не всё телевизионное изображение присутствует на экране просмотра.
Также смотрите статью Overscan на англоязычной Википедии и статью Вылеты развёртки на русскоязычной Википедии.
Parenting (Установка родителя)
Метод моделирования некоторых видов нечётких явлений, которые в противном случае очень трудно было бы воспроизвести при помощи обычных методов визуализации. Наиболее распространёнными примерами являются огонь, взрывы, дым, искры, падающие листья, облака, туман, снег, пыль, хвосты метеоров, звёзды и галактики, либо абстрактные визуальные эффекты, вроде светящихся следов и магических заклинаний. Также используется для моделирования меха, травы или волос.
Phong (Затенение по Фонгу)
Модель локального освещения, которая в определённой степени может помочь добиться реализма трёхмерных объектов путём объединения трёх элементов их освещения: на каждую точку поверхности влияет диффузная, бликовая составляющие и составляющая от окружающей среды. Модель содержит несколько допущений – все источники света являются точками, рассматривается только геометрия поверхности, моделируются только локальные диффузное и бликовое отражения, цвет блика считается таким же, как и цвет источника света, окружающее освещение является глобальной константой.
Pivot Point (Точка вращения)
The pivot point is the point in space around which all rotation, scaling and mirror transformations are centered.
See also the Pivot Point docs.
A list of points in 3D space.
Pose Mode (Режим позы)
Posing (Изменение позы)
Moving, Rotating and Scaling the Bones of an Armature to achieve an aesthetically pleasing pose for a character.
Premultiplied Alpha (Альфа-канал с предумножением)
Primaries (Основные цвета)
Базовый объект, который может использоваться в качестве основы для моделирования более сложных объектов.
Procedural Texture (Процедурная текстура)
В общем случае – текстура, сгенерированная компьютером. Процедурная текстура может быть настроена своими параметрами.
В компьютерной графике в основном используются два вида проекций.
Perspective (Перспективная проекция)
A perspective view is geometrically constructed by taking a scene in 3D and placing an observer at point O. The 2D perspective scene is built by placing a plane (e.g. a sheet of paper) where the 2D scene is to be rendered in front of point O, perpendicular to the viewing direction. For each point P in the 3D scene a PO line is drawn, passing by O and P. The intersection point S between this PO line and the plane is the perspective projection of that point. By projecting all points P of the scene you get a perspective view.
Orthographic (Ортогональная проекция)
For video editing, a proxy is a smaller version of the original file, typically using an optimized video codec and lower resolution version (faster to load) that stands in for the main image or video.
When proxies are built, editing functions like scrubbing and scrolling and compositing is much faster but gives lower resolution and slightly imprecise result.
Quad (Четырёхугольник) Quadrilateral (Четырёхсторонник) Quadrangle (Четырёхугольник)
Quaternion (Кватернион) Quaternion Rotation (Вращение по кватерниону)
Quaternion values can be interpreted geometrically as defining a point on a unit sphere in 4D space. Moving along any great circle of the sphere represents rotating around a fixed axis, with one full circle matching two full rotations.
A global lighting method that calculates patterns of light and shadow for rendering graphics images from three-dimensional models. One of the many different tools which can simulate diffuse lighting in Blender.
Также смотрите статью Radiosity (computer graphics) на англоязычной Википедии.
Blender uses pseudo random number generators, which produce numbers that appear to be random, but given the same initial condition, they will always produce the exact same sequence of numbers.
This is a critical feature to get reproducible and/or stable effects (otherwise e.g. your hair simulation would change every time you re-run it, without any way to control the outcome).
The seed is a number that represents the initial condition of a random generator, if you change its seed, it will produce a new sequence of pseudo-random numbers.
See also Random seed on Wikipedia.
The change in direction of a wave due to a change in velocity. It happens when waves travel from a medium with a given Index of Refraction to a medium with another. At the boundary between the media, the wave changes direction; its wavelength increases or decreases but frequency remains constant.
Процесс вычислительной генерации двумерного изображения из трёхмерной геометрии.
Модель цвета, основанная на традиционных основных цветах — Красном/Зелёном/Синем (Red/Green/Blue). Также RGB-цвета напрямую поддерживаются большинством компьютерных мониторов.
Система отношений, определяющая характер движения чего-либо. Также акт построения такой системы.
Roll (Крен) Roll Angle (Угол крена)
In real CMOS cameras the sensor is read out with scanlines and hence different scanlines are sampled at a different moment in time. This, for example, make vertical straight lines being curved when doing a horizontal camera pan. See also Rolling Shutter on Wikipedia.
Roughness Map (Карта шероховатости)
Scanline (Сканирование строк)
Scene Referenced (Представимое в сцене)
Изображение, чей яркостный канал ничем не ограничивается.
Процесс изменения цвета объекта/поверхности в трёхмерной сцене на основе направления на источник света и расстояния до источника света для создания фотореалистичного эффекта.
Defines how Faces are shaded. Faces can be either solid (faces are rendered flat) or smooth (faces are smoothed by interpolating the normal on every point of the face).
Specular Light (Зеркальное освещение, бликовое освещение)
Освещение, которое отражается преимущественно в одном направлении, как в зеркале. Также используется для обозначения бликов на отражающих объектах.
SSS Subsurface Scattering (Подповерхностное рассеивание)
Механизм распространения света, когда он проникает под поверхность полупрозрачного объекта, рассеивается там, взаимодействуя с материалом, и выходит на поверхность в другой точке. Все неметаллические материалы в какой-то степени являются полупрозрачными. В частности, материалы вроде мрамора, кожи или молока очень трудно реалистично имитировать, если не принимать во внимание подповерхностное рассеивание.
Straight Alpha (Чистый альфа-канал)
Subdiv Subdivision Surface (Подразделение поверхности)
Метод создания сглаженных высокополигональных поверхностей, на вход которого поступает низкополигональная полисетка.
Также смотрите статью Catmull-Clark subdivision surface на англоязычной Википедии.
Техника добавления дополнительной геометрии к полисетке. Она создаёт новые вершины на подразделённых рёбрах, новые рёбра между подразделениями и новые грани на этих рёбрах. Если новые рёбра пересекаются, на месте их пересечения создаётся новая вершина.
Swing Swing and Twist
Refers to decomposition of an arbitrary rotation into a sequence of two single axis rotations: a swing rotation that aims a chosen axis in its final direction using the shortest possible rotation path, followed by a twist rotation around that axis.
In the Quaternion representation the swing rotation always has 0 as the X/Y/Z component corresponding to the selected axis, while twist always has 0 as the other two components.
Определяет визуальные шаблоны поверхностей и имитирует их физическую структуру.
Texture Space (Текстурное пространство)
Ограничивающая рамка, используемая с отображением Сгенерировать для добавления текстуры на изображение.
Timecode (Временной код, код времени)
A coded signal on videotape or film giving information about the frame number and time the frame was recorded. Timecodes are used to sync media between different recording devices, including both audio and video.
Title Safe (Отступы для заголовка)
Область экрана, видимая на всех устройствах. Размещайте текст и графику внутри неё, чтобы быть уверенным, что они не будут обрезаны.
Определяет отношения между поверхностью полисетки и двумерной текстурой. Более подробно, каждая грань полисетки отображается на соответствующую область текстуры. Также возможно (и это часто практикуется) отображать несколько граней полисетки на одни и те же или перекрывающиеся области текстуры.
Vertex (Вершина) Vertices (Вершины)
Vertex Group (Группа вершин)
A cubic 3D equivalent to the square 2D pixel. The name is a combination of the terms «Volumetric» and « Pixel ». Used to store smoke and fire data from physics simulations.
Walk Cycle (Цикл ходьбы)
В анимации цикл ходьбы представляет собой персонажа, имеющего из анимаций только движение ходьбы. В дальнейшем в процессе анимации персонаж помещается в окружающую среду и анимируются остальные движения.
Weight Painting (Рисование весов)
White Point (Точка белого)
Контрольное значение для белого света, определяемое таким образом, что бы оно получалось при равномерном смешении всех основных цветов указанной цветовой модели.
A white point is defined by a set of CIE illuminates which correspond to a color temperature. For example, D65 corresponds to 6500 K light, D70 corresponding to 7000 K and so on.
World Space (Пространство мира)
Raster-based storage of the distance measurement between the camera and the surface points. Surface points which are in front of the camera have a positive Z value and points behind have negative values. The Z-depth map can be visualized as a grayscale image.
© Авторские права : This page is licensed under a CC-BY-SA 4.0 Int. License