no ip proxy arp cisco что это
Безопасность. Начало 05. Cisco Configuration Professional
CCP в определённом смысле упрощает администрирование. В большинстве случаев это действительно помогает новичкам, хотя и для профессионалов здесь есть кое чего интересное.
Например в отличие от CLI, GUI предоставляет в основном только самые нужные и часто используемые настройки, которые легко «подглядеть» взглянув на страницу настроек какой-либо функции. В CLI это сделать невозможно, точнее команда CLI «?» вывалит всевозможные команды, половина из которых не нужна и может быть даже вредна.
С другой стороны CCP не позволяет делать иногда необходимые тонкие настройки и не затрагивает целые функции.
CCP существует в двух вариациях:
Отметим также, что CCP не требует каких либо лицензий и может быть загружен с сайта циски под валидным CCO account.
Установка CCP Express
Cisco CP Express или Cisco CP Express Admin View является облегченной версией CCP с очень ограниченными функциями и устанавливаемый непосредственно на Flash-карту роутера.
Подготовка маршрутизатора к работе с Cisco Configuration Professional (Express)
Для работы CCP (и CCP Express) необходимо выполнить определенные подготовительные действия на маршрутизаторе:
Маршрутизатор должен быть включен и доступен по сети.
Вообще по умолчанию маршрутизатор будет доступен по адресу 10.10.10.1.
Компьютер можно подключить к маршрутизатору используя Cross-кабель и дать адрес например 10.10.10.100 255.255.255.0
10.10.10.1 должен пинговаться. Затем мы заходим через telnet на 10.10.10.1 и выполняем следующие команды:
(1) Включаем на маршрутизаторе сервер HTTP и HTTPS:
Router> enable
Router# conf t
Router(config)# ip http server
Router(config)# ip http secure−server
Router(config)# ip http authentication local
(2) Создаем пользователя с privilege level 15:
Router(config)# username username privilege 15 password 0 password
(3) Настраиваем SSH и Telnet:
Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config−line)# privilege level 15
Router(config−line)# login local
Router(config−line)# transport input telnet
Router(config−line)# transport input telnet ssh
Router(config−line)# exit
(4) Включаем local logging для поддержки log monitoring
Router(config)# logging buffered 51200 warning
После выполнения этих действий мы сможем подключаться к маршрутизатору через Cisco Configuration Professional.
Cisco Configuration Professional Express
Зайти на роутер можно по следующему адресу:
https://router_address
Cisco Configuration Professional Express позволяет управлять лишь ограниченными функциями например:
Cisco Configuration Professional
Полноценный Cisco Configuration Professional позволяет выполнять практически все основные функции.
CCP можно скачать с сайта Cisco при наличии активной подписки.
Здесь для начала в Community мы введем IP нашего роутера, а также имя и пароль учетки для администрирования.
Далее жмем кнопку Discovery.
После выполнения Discovery нам станут доступны опции Configure и Monitor. Позволяющие соответственно настраивать и мониторить наш роутер.
Templates
Templates или шаблоны нам помогут если есть необходимость конфигурировать устройства с аналогичными функциями.
User Profiles
Создание профиля:
Application > Create User Profile
Импорт профиля:
Application > Import User Profile
CCP Security Audit
Фича позволяет автоматически проанализировать конфигурацию маршрутизатора, и затем выдать свои рекомендации.
При этом CCP использует IOS auto secure feature, т.е. примерно тоже самое что и команда auto secure full
Запустить Security Audit:
Configure > Security > Security Audit
Security Audit покрывает целый набор вопросов по безопасности, рассмотрим их вкартце:
Unicast RPF on Outside Interfaces позволяет предотвращать IP spoofing.
Протокол прокси-ARP
Параметры загрузки
Содержание
Введение
Предварительные условия
Требования
Данный документ требует понимания принципов работы ARP и Ethernet.
Используемые компоненты
Сведения, содержащиеся в данном документе, касаются следующих версий программного и аппаратного обеспечения:
ПО Cisco IOS ® версии 12.2 (10b)
Маршрутизаторы серии Cisco 2500
Сведения, содержащиеся в данном документе, были получены от устройств, работающих в специальной лабораторной среде. Все устройства, описанные в данном документе, обладают ненастроенной (заданной по умолчанию) конфигурацией. При работе в действующей сети перед применением команды необходимо изучить все возможные последствия ее выполнения.
Условные обозначения
Дополнительные сведения об условных обозначениях в документах см. в статье Условные обозначения, используемые в технической документации Cisco.
Как работает протокол прокси-ARP?
Ниже приведен пример работы прокси-ARP:
Схема сети
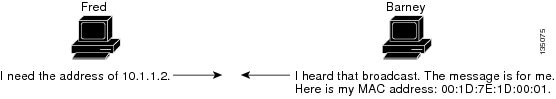
Хосту A (172.16.10.100) подсети A необходимо отправить пакеты хосту D (172.16.20.200) подсети B. Как показано на рисунке выше, у хоста A есть маска подсети a /16. Это значит, что узел А предполагает, что он непосредственно подключен ко всем адресам 172.16.0.0 в сети. Когда хосту А необходимо связаться с устройством, которое предположительно подключено напрямую, он посылает на это устройство ARP-запрос. Таким образом, если хосту A требуется отправить пакет на хост D, который считается подключенным напрямую, хост A отправляет хосту D ARP-запрос.
Для получения доступа к хосту D (172.16.20.200) хосту A нужен MAC-адрес хоста D.
Поэтому хост А передает ARP-запрос в широковещательном режиме на подсеть А, как показано ниже:
Хост A (172.16.10.100) в вышеуказанном запросе ARP запрашивает отправку хостом D (172.16.20.200) своего MAC-адреса. Затем указанный выше пакет запроса ARP инкапсулируется в кадре Ethernet с MAC-адресом хоста A в качестве адреса источника и широковещательной рассылкой (FFFF.FFFF.FFFF) в качестве адреса назначения. Из-за широковещательной рассылки ARP-запрос достигает всех узлов в подсети A, включая интерфейс e0 маршрутизатора, кроме хоста D. Эта рассылка не достигает хоста D, так как маршрутизаторы по умолчанию ее не отправляют.
Поскольку маршрутизатору известно, что целевой адрес (172.16.20.200) находится в другой подсети и достигает хост D, он посылает в ответ собственный MAC-адрес хосту A.
IP адрес отправителя
Выше указан ответ прокси-ARP, который маршрутизатор посылает к хосту A. Ответный пакет прокси-ARP инкапсулируется в кадр Ethernet с MAC-адресом маршрутизатора в качестве адреса источника и с MAC-адресом хоста А в качестве адреса назначения. ARP-ответы являются одноадресными и посылаются узлу, инициировавшему запрос.
При получении ответа ARP хост A обновляет таблицу ARP, как показано ниже:
Теперь хост А будет пересылать все пакеты, которые должны достигнуть 172.16.20.200 (хост D), на MAC-адрес 00-00-0c-94-36-ab (маршрутизатор). Так как маршрутизатору известен путь достижения хоста D, он отправляет пакет этому хосту. ARP-кэш на хостах подсети A загружен MAC-адресом маршрутизатора для всех хостов подсети B. Поэтому все пакеты, предназначенные для подсети B, отправляются маршрутизатору. Маршрутизатор пересылает эти пакеты хостам в подсеть B.
Кэш ARP хоста A представлен ниже:
Примечание. Несколько IP-адресов сопоставляются с одним MAC-адресом (MAC-адресом маршрутизатора), что указывает на использование протокола прокси-ARP.
Интерфейс маршрутизатора Cisco должен быть настроен на прием и отправку прокси-ARP. Этот режим включен по умолчанию. Прокси-ARP отключается командой конфигурирования интерфейса no ip proxy-arp на уровне отдельного интерфейса, как показано ниже:
Чтобы включить прокси-ARP на интерфейсе используйте команду конфигурирования интерфейса ip proxy-arp.
Примечание. Если хост B (172.16.10.200/24) в подсети A пытается отправить пакеты на хост D (172.16.20.200) подсети B, он обращается к таблице IP-маршрутизации и использует соответствующий адрес для маршрутизации. Хост B (172.16.10.200/24) не запускает прокси-ARP для IP-адреса 172.16.20.200 хоста D, так как он принадлежит другой подсети, отличающейся от подсети, настроенной на хосте B интерфейса ethernet 172.16.20.200/24.
Преимущества прокси-ARP
Основное преимущество использования прокси-ARP состоит в том, что этот протокол можно установить на один маршрутизатор в сети без изменения таблиц маршрутизации на остальных маршрутизаторах в той же сети.
Прокси-ARP используется в сети, где IP-хосты не настроены в шлюзе по умолчанию или не обладают интеллектуальными функциями маршрутизации.
Недостатки прокси-ARP
Это увеличивает объем ARP-трафика в вашем сегменте сети.
Хостам необходимы большие ARP-таблицы для обработки сопоставления IP-адресов и MAC-адресов.
Система безопасности может быть нарушена. Один компьютер может выдавать себя за другой для перехвата пакетов. Это называется «спуфингом».
Это не относится к сетям, которые не используют ARP для разрешения адресов.
Это не касается всех сетевых топологий (например, нескольких маршрутизаторов, соединяющих две физические сети).
Для получения более подробных сведений о настройке прокси-ARP см. раздел Включение прокси-ARP документа Настройка IP–адресов.
ARP: Нюансы работы оборудования Cisco и интересные случаи. Часть 2
Привет, Habr! В предыдущей части статьи мы рассмотрели особенности работы ARP на маршрутизаторах Cisco, связанные с правилами NAT и с функцией Proxy ARP. В данном посте попробую разобрать отличия в работе ARP между маршрутизаторами Cisco и межсетевыми экранами Cisco ASA. В заключении статьи поделюсь несколькими интересными случаями из практики, связанными с работой ARP.
NAT и Proxy ARP на межсетевых экранах Cisco ASA
Рассмотрим примеры на основании следующей простейшей топологии:
Настройки интерфейсов Cisco ASA:
Настройки правила NAT и списка доступа на интерфейсе outside:
Как видно из представленных настроек мы публикуем порт tcp 3389 (RDP) под адресом 198.18.99.2, который не принадлежит IP-подсети интерфейса Cisco ASA.
Проверяем опцию sysopt noproxyarp:
Видно, что опция не выставлена (noproxyarp не включён). Попробуем открыть tcp-порт 3389 адреса 198.18.99.2 и одновременно посмотрим сниффер:
Успех: Cisco ASA отвечает на ARP-запрос и порт открывается.
Попробуем выставить опцию sysopt noproxyarp outside. Очищаем arc-cache на компьютере, подключенном к outside-интерфейсу, и пробуем открыть порт снова:
ASA более не отвечает на ARP-запросы к целевому IP-адресу. При этом, не имеет значения, находится ли целевой IP-адрес в IP-подсети интерфейса ASA. При выставленной опции sysopt noproxyarp ASA будет отвечать на ARP-запросы, адресованные исключительно IP-адресу интерфейса.
Не стоит сравнивать настройку ip proxy-arp интерфейса маршрутизатора с настройкой опции sysopt noproxyarp Cisco ASA. Опция Cisco ASA не включает проксирование любых ARP-запросов через межсетевой экран. Эта опция отвечает исключительно за обслуживание внутренних глобальных IP-адресов правил NAT и статических записей в ARP-таблице ASA, настроенных с ключевым словом alias.
В некоторых случаях функционал ARP-ответов необходимо отключать для конкретных правил NAT. Для этого служит ключевое слово no-proxy-arp в настройках NAT. Наиболее распространённый пример – настройка NAT-исключений при использовании VPN на Cisco ASA. Предположим, локальная сеть за Cisco ASA – 192.168.20.0/24, локальная сеть на удалённой стороне Site-to-Site VPN – 192.168.30.0/24. NAT-исключение для данного VPN можно настроить следующим образом:
Представленная конфигурация указывает для Cisco ASA, что IP-подсеть local-LAN 192.168.20.0/24 целиком опубликована на каждом интерфейсе Cisco ASA (any,any в правиле NAT) под внутренними глобальными адресами той же IP-подсети local-LAN. Следовательно, при данной конфигурации Cisco ASA будет отвечать на любой ARP-запрос к целевому IP-адресу из IP-подсети 192.168.20.0/24, поступившему на любой интерфейс, включая inside интерфейс.
Представим ситуацию, хост с адресом 192.168.20.5 хочет обратиться к хосту из той же IP-подсети с адресом 192.168.20.6. Формируется ARP-запрос на целевой адрес 192.168.20.6. ARP-запрос рассылается широковещательно и достигает как целевой хост, так и inside интерфейс Cisco ASA. Настроенное правило NAT заставляет Cisco ASA ответить своим MAC-адресом на ARP-запрос. Если ARP-ответ от Cisco ASA поступит раньше ответа от целевого хоста, весь трафик, направленный к целевому хосту, пойдёт на Cisco ASA, где будет благополучно отброшен.
В представленном примере Cisco ASA будет работать как «black hole» для локальной IP-подсети, стремясь «засасывать» на себя весь трафик. При этом, элемент policy NAT (настройка NAT после ключевых слов destinations static) ситуацию не спасает. Если сравнивать с маршрутизатором, данная настройка на Cisco ASA по эффекту схожа с совместной настройкой ip proxy-arp и ip local-proxy-arp на интерфейсе маршрутизатора. Чтобы избежать описанного эффекта, в правиле NAT на Cisco ASA необходимо добавить ключевое слово no-proxy-arp:
Примечание: описанный эффект можно избежать, указывая в настройках правила NAT точные интерфейсы, вместо ключевых слов any. Например, nat (inside,outside) …
Случай №1. Secondary IP-адрес у провайдера
Подключали к провайдеру межсетевой экран Cisco ASA. Подключение прошло успешно и все сервисы работали корректно. Однако через некоторое время связь пропадала. Детальный анализ показывал, что если инициировать исходящее соединение, то оно работает стабильно (трафик ходит в обе стороны). Проблема появляется только со входящими соединениями из сети Интернет (например, удалённое подключение к маршрутизатору). При этом прослеживается прямая зависимость входящих соединений от исходящих: если есть исходящие соединения, то и входящие соединения начинают корректно работать. Однако, по прошествии некоторого времени подключиться удалённо или «пропинговать» устройство из Интернета снова не удаётся.
Так как с физическим и канальным уровнем предположительно всё в порядке, мы стали проверять работу ARP. Запустили debug arp на ASA и попробовали очистить arp-cache. По debug-сообщениям увидели, что ASA корректно отправляет ARP-запрос и без проблем получает ARP-ответ от провайдера. В данном примере IP нашей ASA 80.X.X.4, её MAC-адрес a0ec.****.****, IP-шлюза провайдера 80.X.X.1, MAC-шлюза провайдера aa43.****.****:
Однако, через какое-то время заметили сообщение в debug arp на ASA:
Судя по данному сообщению ASA получает ARP-запрос с верным Sender MAC Address aa43.****.**** но неверным Sender IP Address – 195.Y.Y.1. Данный некорректный ARP-запрос ASA отбрасывает и не отправляет ARP-ответ.
Таким образом, когда существует исходящий трафик, ASA отправляет ARP-запрос (при необходимости, когда соответствующая запись в ARP-таблице ASA требуется обновления) в сторону провайдера и получает ARP-ответ. Благодаря ARP-запросу от ASA оборудование провайдера также получает запись об ASA в своей ARP-таблице. Однако, когда исходящий трафик от ASA отсутствует продолжительное время и ASA не отправляет ARP-запрос, на оборудовании провайдера в ARP-таблице запись об ASA истекает. Оборудование провайдера пробует обновить запись, отправляя ARP-запрос, но ответ не получает. Отсюда и появляются «плавающие» проблемы со связью.
Осталось понять, почему оборудование провайдера отправляет ARP-запрос с неверным Sender IP Address. Позже провайдер проверил данную ситуацию со своей стороны и даже показал дамп ARP-трафика, который подтверждал debug-сообщения ASA:
Оказалось, что на интерфейсе провайдера адрес 195.Y.Y.1 был настроен как основной, а IP-адрес 80.X.X.4, который являлся для нас шлюзом по умолчанию, был настроен как secondary. Эта настройка полностью объясняла ситуацию. В данном случае проблема была решена добавлением статической ARP-записи на оборудовании провайдера.
Абсолютно аналогичная ситуация у нас возникала на другой площадке, когда мы использовали для подключения к провайдеру маршрутизатор Cisco. На оборудовании провайдера наш шлюз был также настроен как seconday IP-адрес. В этом случае, чтобы ускорить процесс решения проблемы, мы добавили на маршрутизаторе secondary IP-адрес из той же подсети, что и основной IP-адрес на интерфейсе провайдера. После этого наш маршрутизатор стал успешно отвечать на ARP-запросы со стороны провайдера, так как на нашем интерфейсе появился IP-адрес из той же подсети, что и адрес в ARP-запросе.
Случай №2. ARP-несовместимость
Перед нами была поставлена задача в одном из офисов заменить маршрутизатор Cisco ISR на межсетевой экран Cisco ASA. Межсетевой экран ASA предварительно был настроен и отправлен в точку установки. После подключения к провайдеру Cisco ASA оказался недоступным для удалённого подключения. На первый взгляд на устройстве всё работало корректно. Межсетевой экран ASA корректно определял MAC адрес маршрутизатора провайдера с помощью стандартной процедуры ARP-запрос/ARP-ответ. Пакеты уходили с внешнего интерфейса устройства в Интернет. При этом в обратную сторону на ASA ничего не приходило. Этот факт фиксировался встроенными средствами перехвата пакетов (packet capture).
После обращения к провайдеру было установлено, что пакеты от ASA успешно доставлялись на оборудование провайдера, также провайдер видел ответные пакеты, приходящие с вышестоящего оборудования. После того как был обратно подключен маршрутизатор, трафик снова начал ходить корректно в обе стороны. Это означало, что проблема где-то на стыке между провайдером и межсетевым экраном ASA. После повторного обращения к провайдеру с детальным описанием проблемы было определено, что оборудование провайдера не видит MAC адрес межсетевого экрана ASA. Собранный демо-стенд доказал корректность работы ASA (роль провайдера играл маршрутизатор Cisco). По какой-то причине устройство провайдера не заносило запись об ASA в ARP-таблицу после получения ARP-ответа от ASA. Самое интересное, что ARP-запрос, поступающий от Cisco ASA не отбрасывался. Оборудование провайдера корректно отвечало на ARP-запрос от ASA, но также, не заносило запись ASA в ARP-таблицу.
В итоге провайдеру было предложено сделать статическую привязку в таблице ARP. Данный случай показал несовместимость по ARP оборудования провайдера с межсетевым экраном Cisco ASA. К сожалению, провайдер не озвучил производителя своего оборудования.
Случай №3. Gratuitous ARP
И опять подключаем к провайдеру Cisco ASA. В этот раз вместо сервера MS TMG. Особенность данного случая в том, что MS TMG был подключен к устройству провайдера через L2-коммутатор. Предполагалось подключение ASA также через L2-коммутатор:
Итак, отключаем MS TMG и вместо него в тот же порт L2-коммутатора подключаем Cisco ASA. Видим стандартную ситуацию: с внешнего порт Cisco ASA трафик уходит, но ответные пакеты отсутствуют. После обращения к провайдеру выясняется, что оборудование провайдера по-прежнему видит MAC-адрес сервера MS TMG за IP-адресом, перешедшим на Cisco ASA.
Дальнейшее разбирательство показало, что межсетевой экран Cisco ASA не шлёт Gratuitous ARP сообщение при переходе интерфейса из состояния DOWN в состояние UP. А так как оборудование провайдера подключено через L2-коммутатор, при смене устройства на нашей стороне канал до провайдера не падает, и интерфейс маршрутизатора провайдера всегда остаётся во включенном состоянии. Единственный способ своевременно оповестить провайдера о том, что на нашей стороне изменилось устройство и MAC-адрес, – Gratuitous ARP. В противном случае, придётся ждать таймаута ARP-записи у провайдера, а это как, как правило, 4 часа.
В данном случае мы сделали на интерфейсе Cisco ASA команды no ip address, ip address x.x.x.x y.y.y.y. После этого ASA всё же отправила Gratuitous ARP, и всё взлетело.
В данной статье, состоящей из двух частей, я постарался рассмотреть тонкости работы ARP на оборудовании Cisco в случаях использования трансляции сетевых адресов (NAT), а также функционал Proxy ARP. Разобрал отличия в работе ARP между маршрутизаторами Сisco и межсетевыми экранами Cisco ASA. В заключении статьи я рассмотрел проблемы, возникающие при подключении к Интернет-провайдеру, обусловленные работой ARP.
Описанные случаи показывают, на сколько важно помнить о необходимости проверки ARP в процессе решения и устранения сетевых проблем. Надеюсь, материал данной статьи станет полезным для более глубокого понимания работы ARP.
Жду комментарии. Может быть кто-то сможет рассказать собственные интересные случаи, связанные с работой ARP.
IP Addressing: ARP Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15M&T
Book Title
IP Addressing: ARP Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15M&T
Chapter Title
Address Resolution Protocol
View with Adobe Reader on a variety of devices
View in various apps on iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader, or Windows Phone
Results
Chapter: Address Resolution Protocol
Address Resolution Protocol
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) feature performs a required function in IP routing. ARP finds the hardware address, also known as Media Access Control (MAC) address, of a host from its known IP address. ARP maintains a cache (table) in which MAC addresses are mapped to IP addresses. ARP is part of all Cisco systems that run IP.
This feature module explains ARP for IP routing and the optional ARP features you can configure, such as static ARP entries, timeout for dynamic ARP entries, clearing the cache, and proxy ARP.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About the Address Resolution Protocol
Layer 2 and Layer 3 Addressing
IP addressing occurs at Layer 2 (data link) and Layer 3 (network) of the Open System Interconnection (OSI) reference model. OSI is an architectural network model developed by ISO and ITU-T that consists of seven layers, each of which specifies particular network functions such as addressing, flow control, error control, encapsulation, and reliable message transfer.
Layer 2 addresses are used for local transmissions between devices that are directly connected. Layer 3 addresses are used for indirectly connected devices in an internetwork environment. Each network uses addressing to identify and group devices so that transmissions can be sent and received. Ethernet (802.2, 802.3, Ethernet II, and Subnetwork Access Protocol [SNAP]), Token Ring, and Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) use media access control (MAC) addresses that are «burned in» to the network interface card (NIC). The most commonly used network types are Ethernet II and SNAP.
 Note | For the supported interface types, see the data sheet for your hardware platform. |
In order for devices to be able to communicate with each when they are not part of the same network, the 48-bit MAC address must be mapped to an IP address. Some of the Layer 3 protocols used to perform the mapping are:
For the purposes of IP mapping, Ethernet, Token Ring, and FDDI frames contain the destination and source addresses. Frame Relay and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networks, which are packet-switched, data packets take different routes to reach the same destination. At the receiving end, the packet is reassembled in the correct order.
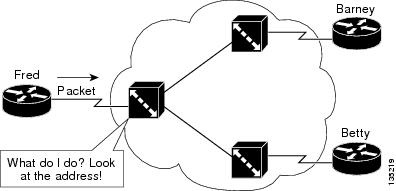
In a Frame Relay network, there is one physical link that has many logical circuits called virtual circuits (VCs). The address field in the frame contains a data-link connection identifier (DLCI), which identifies each VC. For example, in the figure below, the Frame Relay switch to which device Fred is connected receives frames; the switch forwards the frames to either Barney or Betty based on the DLCI that identifies each VC. So Fred has one physical connection but multiple logical connections.
| Figure 1 | Frame Relay Network |
ATM networks use point-to-point serial links with the High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) protocol. HDLC includes a meaningless address field included in five bytes of the frame header frame with the recipient implied since there can be only one.
Overview of the Address Resolution Protocol
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) was developed to enable communications on an internetwork and is defined by RFC 826. Layer 3 devices need ARP to map IP network addresses to MAC hardware addresses so that IP packets can be sent across networks. Before a device sends a datagram to another device, it looks in its ARP cache to see if there is a MAC address and corresponding IP address for the destination device. If there is no entry, the source device sends a broadcast message to every device on the network. Each device compares the IP address to its own. Only the device with the matching IP address replies to the sending device with a packet containing the MAC address for the device (except in the case of «proxy ARP»). The source device adds the destination device MAC address to its ARP table for future reference, creates a data-link header and trailer that encapsulates the packet, and proceeds to transfer the data. The figure below illustrates the ARP broadcast and response process.
| Figure 2 | ARP Process |
When the destination device lies on a remote network, one beyond another Layer 3 device, the process is the same except that the sending device sends an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway. After the address is resolved and the default gateway receives the packet, the default gateway broadcasts the destination IP address over the networks connected to it. The Layer 3 device on the destination device network uses ARP to obtain the MAC address of the destination device and delivers the packet.
Encapsulation of IP datagrams and ARP requests and replies on IEEE 802 networks other than Ethernet use Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP).
The ARP request message has the following fields:
ARP Caching
Because the mapping of IP addresses to media access control (MAC) addresses occurs at each hop (Layer 3 device) on the network for every datagram sent over an internetwork, performance of the network could be compromised. To minimize broadcasts and limit wasteful use of network resources, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) caching was implemented.
ARP caching is the method of storing network addresses and the associated data-link addresses in memory for a period of time as the addresses are learned. This minimizes the use of valuable network resources to broadcast for the same address each time a datagram is sent. The cache entries must be maintained because the information could become outdated, so it is critical that the cache entries are set to expire periodically. Every device on a network updates its tables as addresses are broadcast.
There are static ARP cache entries and dynamic ARP cache entries. Static entries are manually configured and kept in the cache table on a permanent basis. Static entries are best for devices that have to communicate with other devices usually in the same network on a regular basis. Dynamic entries are added by Cisco software, kept for a period of time, and then removed.
Static and Dynamic Entries in the ARP Cache
Static routing requires an administrator to manually enter IP addresses, subnet masks, gateways, and corresponding media access control (MAC) addresses for each interface of each device into a table. Static routing enables more control but requires more work to maintain the table. The table must be updated each time routes are added or changed.
Dynamic routing uses protocols that enable the devices in a network to exchange routing table information with each other. The table is built and changed automatically. No administrative tasks are needed unless a time limit is added, so dynamic routing is more efficient than static routing. The default time limit is 4 hours. If the network has a great many routes that are added and deleted from the cache, the time limit should be adjusted.
The routing protocols that dynamic routing uses to learn routes, such as distance-vector and link-state, is beyond the scope of this document.
Devices That Do Not Use ARP
When a network is divided into two segments, a bridge joins the segments and filters traffic to each segment based on Media Access Control (MAC) addresses. The bridge builds its own address table, which uses MAC addresses only, as opposed to a router, which has an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache that contains both IP addresses and the corresponding MAC addresses.
Passive hubs are central-connection devices that physically connect other devices in a network. They send messages out all ports to the devices and operate at Layer 1, but they do not maintain an address table.
Layer 2 switches determine which port is connected to a device to which the message is addressed and send the message only to that port, unlike a hub, which sends the message out all its ports. However, Layer 3 switches are routers that build an ARP cache (table).
Inverse ARP
Inverse ARP, which is enabled by default in ATM networks, builds an ATM map entry and is necessary to send unicast packets to a server (or relay agent) on the other end of a connection. Inverse ARP is supported only for the aal5snap encapsulation type.
For multipoint interfaces, an IP address can be acquired using other encapsulation types because broadcast packets are used. However, unicast packets to the other end will fail because there is no ATM map entry and thus DHCP renewals and releases also fail.
For more information about Inverse ARP and ATM networks, see the «Configuring ATM» feature module in the Asynchronous Transfer Mode Configuration Guide.
Reverse ARP
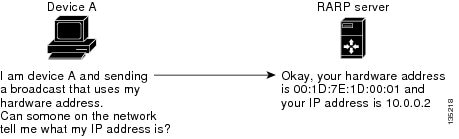
Reverse ARP (RARP) as defined by RFC 903 works the same way as the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), except that the RARP request packet requests an IP address instead of a media access control (MAC) address. RARP often is used by diskless workstations because this type of device has no way to store IP addresses to use when they boot. The only address that is known is the MAC address because it is burned in to the hardware.
RARP requires a RARP server on the same network segment as the device interface. The figure below illustrates how RARP works.
| Figure 3 | RARP Process |
Because of the limitations with RARP, most businesses use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign IP addresses dynamically. DHCP is cost-effective and requires less maintenance than RARP. The most important limitations with RARP are as follows:
Cisco software attempts to use RARP if it does not know the IP address of an interface at startup to respond to RARP requests that it is able to answer. The AutoInstall feature of the software automates the configuration of Cisco devices.
AutoInstall supports RARP and enables a network manager to connect a new device to a network, turn it on, and automatically load a pre-existing configuration file. The process begins when no valid configuration file is found in NVRAM. For more information about AutoInstall, see the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Proxy ARP
Proxy Address Resolution Protocol, as defined in RFC 1027, was implemented to enable devices that are separated into physical network segments connected by a router in the same IP network or subnetwork to resolve IP-to-MAC addresses. When devices are not in the same data link layer network but are in the same IP network, they try to transmit data to each other as if they were on the local network. However, the router that separates the devices will not send a broadcast message because routers do not pass hardware-layer broadcasts. Therefore, the addresses cannot be resolved.
Proxy ARP is enabled by default so the «proxy router» that resides between the local networks responds with its MAC address as if it were the router to which the broadcast is addressed. When the sending device receives the MAC address of the proxy router, it sends the datagram to the proxy router, which in turns sends the datagram to the designated device.
Proxy ARP is invoked by the following conditions:
When proxy ARP is disabled, a device responds to ARP requests received on its interface only if the target IP address is the same as its IP address or if the target IP address in the ARP request has a statically configured ARP alias.
Serial Line Address Resolution Protocol
Serial Line ARP (SLARP) is used for serial interfaces that use High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) encapsulation. A SLARP server, intermediate (staging) device, and another device providing a SLARP service might be required in addition to a TFTP server. If an interface is not directly connected to a server, the staging device is required to forward the address-resolution requests to the server. Otherwise, a directly connected device with SLARP service is required. Cisco software attempts to use SLARP if it does not know the IP address of an interface at startup to respond to SLARP requests that software is able to answer.
Cisco software automates the configuration of Cisco devices with the AutoInstall feature. AutoInstall supports SLARP and enables a network manager to connect a new device to a network, turn it on, and automatically load a pre-existing configuration file. The process begins when no valid configuration file is found in NVRAM. For more information about AutoInstall, see the Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
 Note | AutoInstall supports serial interfaces that use Frame Relay encapsulation. |
Authorized ARP
How to Configure the Address Resolution Protocol
By default, the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) feature is enabled and is set to use Ethernet encapsulation. Perform the following tasks to change or verify ARP functionality:
Enabling the Interface Encapsulation
Perform this task to support a type of encapsulation for a specific network, such as Ethernet, Frame Relay, FDDI, or Token Ring. When Frame Relay encapsulation is specified, the interface is configured for a Frame Relay subnetwork with one physical link that has many logical circuits called virtual circuits (VCs). The address field in the frame contains a data-link connection identifier (DLCI) that identifies each VC. When SNAP encapsulation is specified, the interface is configured for FDDI or Token Ring networks.
 Note | The encapsulation type specified in this task should match the encapsulation type specified in the «Defining Static ARP Entries» task. |
SUMMARY STEPS
2. configure terminal
3. interface type number
DETAILED STEPS